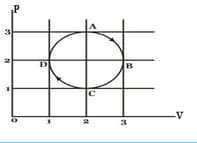
The figure shows the p-V plot an ideal gas taken through a cycle ABCDA. The part ABC is a semi - circle and CDA is half of an ellipse. Then,
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
[ is the gas constant]
It rejects of heat during and absorbs of heat during . During , there is no transfer of heat and of work is done by the gas. What should be the area of the closed curve
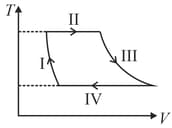
For the given cyclic process as shown for a gas, the work done is:
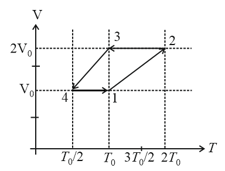
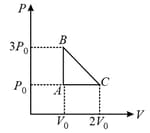
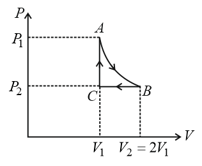
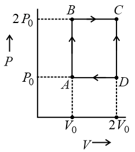
mole of a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process (see figure) consisting of the following processes.
Isothermal expansion at temperature so that the volume is doubled from to and pressure changes from to
Isobaric compression at pressure to initial volume
Isochoric change leading to change of pressure from to
Total work done in the complete cycle is:
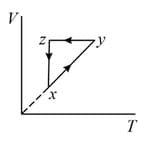
The - diagram that best describes this cycle is: (Diagrams are schematic and not to scale)
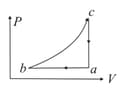
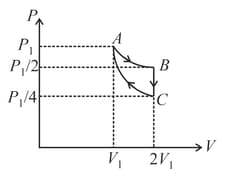
If one mole of an ideal gas at is allowed to expand reversibly and isothermally ( to ) its pressure is reduced to one-half of the original pressure (see figure). This is followed by a constant volume cooling till its pressure is reduced to one-fourth of the initial value Then it is restored to its initial state by a reversible adiabatic compression ( to ). The net workdone by the gas is equal to:
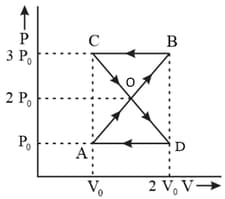
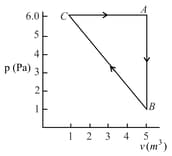
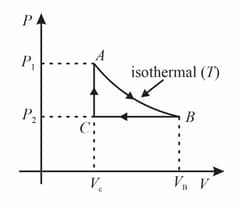
One mole of an ideal gas is taken around the complete cycle as shown in the PV-diagram. Considering the universal gas constant R, the work done by the gas in one complete cycle is:
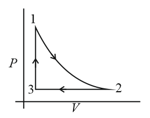
The heat energy absorbed by a system is going through a cyclic process shown in the figure. The work done during the process is
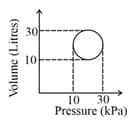
(Take , where is gas constant)
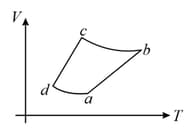
The corresponding P - V diagram for the process is (all figures are schematic and not drawn to scale) :