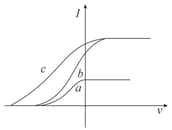
The figure shows the variation of photocurrent with anode potential for a photosensitive surface for three different radiations. Let Ia, Ib and Ic be the intensities and fa, fb and fc be the frequencies for the curves a, b and c respectively
Important Questions on Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
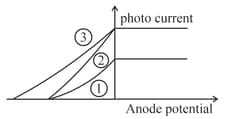
The following graph represents the variation of photo current with anode potential for a metal surface. Here and represents intensities and represents frequency for curves and respectively, then
The photoelectric threshold for a certain metal surface is . If the metal surface is irradiated by a wavelength of , the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is
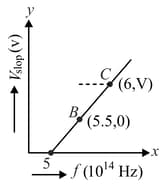
Given figure shows few data points in a photo-electric effect experiment for a certain metal. The minimum energy for ejection of electrons from its surface is: (Planck's constant )
The work function of three photosensitive materials used to build photoelectric devices are given as : Sodium copper and gold Which of the following statements is correct. (The frequency of visible light lies in the range to

