The following occur during the response to infection:
1. Attachment of bacteria to cell surface membrane of phagocyte.
2. Movement of phagocyte to site of infection by bacteria.
3. Formation of phagocytic vacuole.
4. Fusion of lysosomes to the phagocytic vacuole.
5. Infolding of cell surface membrane.
6. Release of enzymes into the phagocytic vacuole.

Important Questions on Immunity
Tetanus is a bacterial disease that may be acquired during accidents in which a wound is exposed to the soil.
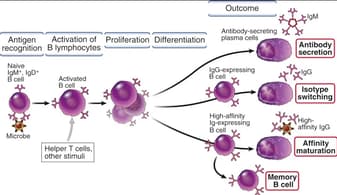
B-lymphocytes originate from the stem cells in bone marrow, mature and circulate around the body. Following infection by tetanus bacteria, some B-lymphocytes will become activated as shown in the diagram.
Explain the role of stem cells in the production of lymphocytes.
or reload the browser
or reload the browser
Tetanus is a bacterial disease that may be acquired during accidents in which a wound is exposed to the soil.
B-lymphocytes originate from the stem cells in bone marrow, mature and circulate around the body. Following infection by tetanus bacteria, some B-lymphocytes will become activated as shown in the diagram.
.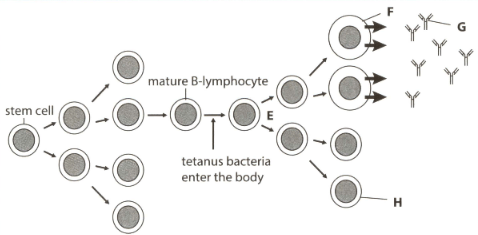
Explain how cell H is responsible for long-term immunity to tetanus.
Phagocytes and lymphocytes are both present in samples of blood.
Describe how the structure of a phagocyte differs from the structure of a lymphocyte.
The diagram shows an antibody molecule.
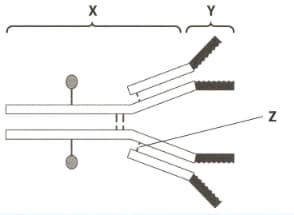
The regions X and Y.
The diagram shows an antibody molecule.
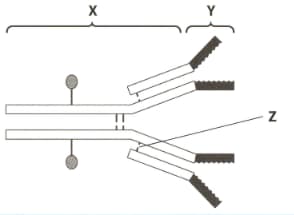
The bond labelled Z.
