The internal and external pressures for a soap bubble are same. The surface tension of soap solution is and its diameter is . Determine the charge on soap bubble.
Important Questions on Electrostatics
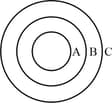
Three concentric spherical shells are arranged as shown in the figure. The innermost and outermost spheres are connected to earth. If the middle sphere is given a charge . the charges induced in the innermost and outermost spheres respectively are
Conventionally which coloured wire is used for earthing?
Given below are two statements.
Statement I : Electric potential is constant within and at the surface of each conductor.
Statement II : Electric field just outside a charged conductor is perpendicular to the surface of the conductor at every point.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options give below.
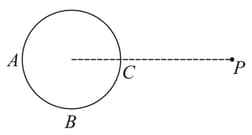
A hollow conducting sphere is placed in an electric field produced by a point charge placed at as shown in figure. Let be the potentials at points and , respectively. Then
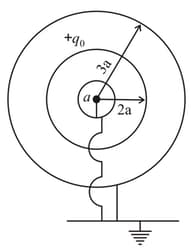
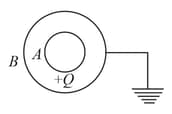
A spherical conductor is placed concentrically inside a hollow spherical conductor . The charge is given to and is earthed. Then the electric field is not zero
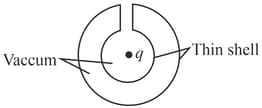
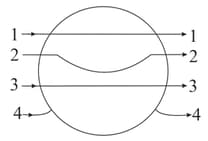
Which one of the following figures correctly indicates the induced charge distribution in the conductor (ignore edge effects).
Consider an initially neutral hollow conducting spherical shell with inner radius and outer radius A point charge is now placed inside the shell at a distance from the center. The shell is then grounded by connecting the outer surface to the earth. P is an external point at a distance from the point charge on the line passing through the center and the point charge as shown in the figure.
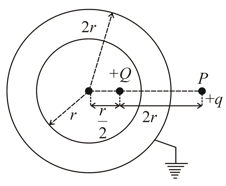
The magnitude of the force on a test charge placed at P will be
Reason: The total transfer of charge from one to another is not possible.
Reason: In metal, induced electric field is equal and opposite of applied field.
Reason: In the above assertion electric potential is constant inside the conductor in static condition.
Assertion: When a charged body is brought near a neutral conducting body, the induced charge that appears on the nearer surface of the conducting body is always equal and opposite to the charge that has been brought near to it.
Reason: Net electric field inside the conductor is zero.

