The most common ingredients of freezing mixture are water and .
Important Questions on Calorimetry and Change of State
A thermally insulated cubical box of side length and wall thickness containing of ice is closed on all sides. The mass of ice melted in hours is (Thermal conductivity of the material of the box latent heat of ice and ambient temperature )
Explain why, with reference to high latent heat of fusion of ice: Rivers fed by water from snow covered mountains are not likely to dry up in summer.
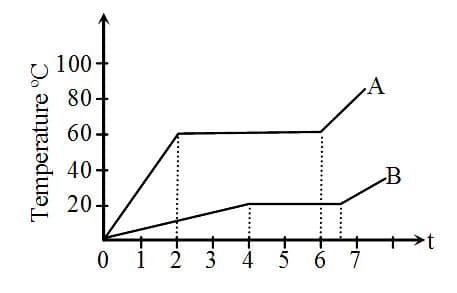
During the change of state of a substance, the temperature remains unchanged, although the heat is supplied or withdrawn. Explain it on the basis of kinetic theory. Explain the physical difference between solids, liquids and gases on the basis of molecular forces.
[Given specific heat of water is 4.2 kJ/kg]
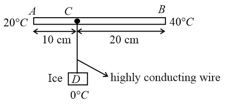
In the figure shown is rod of length and area of cross-section and thermal conductivity of S.I. units. The ends and are maintained at temperature and respectively. A point of this rod is connected to a box , containing ice at , through a highly conducting wire of negligible heat capacity. The rate at which ice melts in the box is . The rate of heat flow through is and the rate of heat flow through is z. Then,
[Assume latent heat of fusion for ice ]
J = 4.2 J/cal).
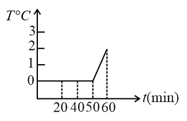
Amount of heat required to convert 10 g of ice to water at 20 is