EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
The primary structure of protein describes how the different -amino acids are linked to each other in a linear chain. Draw the structures of two different dipeptides that can be formed when glycine reacts with serine.

Important Questions on Biochemistry
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
The tertiary structure of protein describe the overall folding of the chains to give the protein its three-dimensional shape.This is caused by interactions between the side-chains of amino acid residues. Consider the two segments of a polypeptide chain shown in figure.
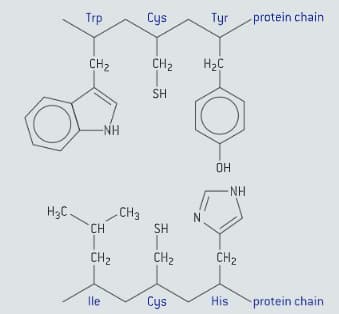
Deduce the type of interaction that can occur between the side-chains of Trp and Ile, Cys and Cys, and Tyr and His.
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
