The pulley (uniform disc) shown in figure has, radius and moment of inertia about its axis ( and both move)
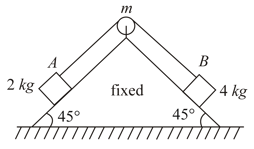
(a) Assuming all the plane surfaces are smooth and there is no slipping between pulley and string, calculate the acceleration of the mass .
(b) The friction coefficient between the block and the plane below is and the plane below the block is frictionless. Assuming no slipping between pulley and string find acceleration of block. Take .


Important Questions on Laws of Motion
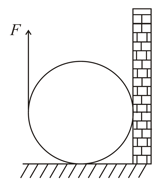
Figure shows a vertical force that is applied tangentially to a uniform cylinder of weight . The coefficient of static friction between the cylinder and all surfaces is . Find in terms of , the maximum force that can be applied without causing the cylinder to rotate.
A wedge of mass and triangular cross section is moving with a constant velocity- towards a sphere of radius fixed on a smooth horizontal table as shown in the figure. The wedge makes an elastic collision with the fixed sphere and returns along the same path without any rotation. Neglect all friction and suppose that the wedge remains in contact with the sphere for a very short time , during which the sphere exerts a constant force on the wedge. The sphere is always fixed.
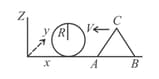
(a) Find the force and also the normal force exerted by the table on the wedge during the time .
(b) Let denote the perpendicular distance between the centre of mass of the wedge and the line of action of force . Find the magnitude of the torque due to the normal force about the centre of the wedge, during the time .
A particle of mass is moving in the plane such that its and coordinates vary according to the law, where and are positive constants and is time. Find,
(a) equation of the path. Name the trajectory (path),
(b) whether the particle moves in clockwise or anticlockwise direction,
(c) magnitude of the force on the particle at any time .
