The reflecting rays meet on the principal axis of the mirror. This point is called the _____ of the concave mirror.
Important Questions on Light- Reflection and Refraction
What is meant by the pole of a spherical mirror?
Correct relation between radius of curvature() and Focal length () of a spherical mirror is:
Observe the following diagram and answer the question given below
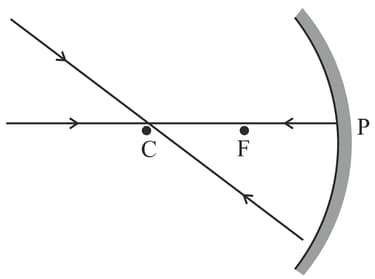
Explain why a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected back along the same path.
A concave mirror of focal length 15cm forms an image. The position of the object when the image is virtual and linear magnification is 2 is.
What will be the angle of incidence when a ray of light passes through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror?
A student holding a mirror in his hand, directed the reflecting surface of the mirror towards the Sun. He then directed the reflected light on to a sheet of paper held close to the mirror.
Will he be able to determine the approximate value of focal length of this mirror from this activity ? Give reason and draw ray diagram to justify your answer in this case.

