The slope of a velocity-time graph gives
Important Questions on Motion
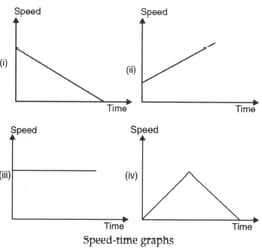
In the given fig., four cases of the speed-time graph are given. In which case is the speed constant? In which case is the speed increasing? In which case is the speed decreasing? What happens in the fourth case?
Draw the velocity-time graphs for the following situations:
(a) When the body is moving with a uniform velocity.
(b) When the body is moving with a variable velocity and uniform acceleration.
(c) When the body is moving with a variable (non-uniform) velocity and uniform deceleration.
(d) When the body is moving with a variable velocity and variable acceleration.
Differentiate between speed-time graph and velocity-time graph of a body thrown vertically upward.
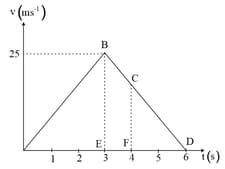
The velocity-time graph of a block moving on a horizontal surface is shown below. The mass of the block is . What is the force acting on the block?
Study the velocity-time graph and calculate:
(a) The acceleration from to
(b) The acceleration from to
(c) The distance covered in region
(d) The average velocity from to
(e) The distance covered in region .
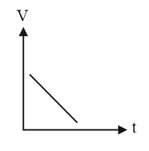
Interpret the nature of force acting on a body whose motion is represented by the following velocity-time graph.
The speed-time graph for a car is shown in figure.
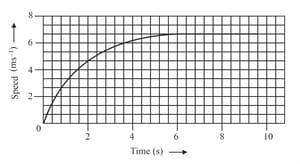
Find how far the car travels in the first . Shade, the area on the graph that represents the distance, travelled by car during the period.
What type of motion is represented by the following graph?
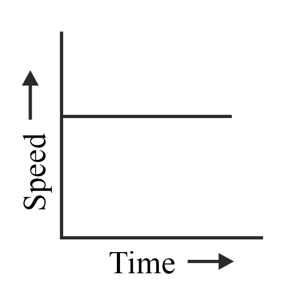
What type of motion is represented by the following graph?
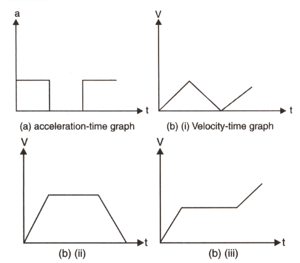
The acceleration-time graph for a body is shown in fig.(a). Which of the following figures from fig.(b) would show the velocity-time graph for the same body?