HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
The specific heats, and of a gas of diatomic molecules, are given (in units of ) by and respectively. Another gas of diatomic molecules, has the corresponding values and If they are treated as ideal gases, then:
(a) has one vibrational mode and has two
(b) has a vibrational mode but has none.
(c)Both and have a vibrational mode each.
(d) is rigid but has a vibrational mode.
52.73% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A gas can be taken from to via two different processes and .
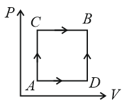
When path is used of heat flows into the system and of work is done by the system. If the path is used then work done by the system is , the heat flows into the system in the path is:
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
moles of an ideal gas with constant volume heat capacity undergo an isobaric expansion by certain volume. The ratio of the work done in the process, to the heat supplied is:
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A cylinder with fixed capacity of litre contains helium gas at STP. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of the gas by is:
[Given that
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
When heat is supplied to a diatomic gas of rigid molecules, at constant volume its temperature increases by . The heat required to produce the same change in temperature, at a constant pressure is:
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Half mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is heated at a constant pressure of from to . Work done by the gas isGas constant,)
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Two moles of helium gas is mixed with three moles of hydrogen molecules (taken to be rigid). What is the molar specific heat of mixture at constant volume?
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
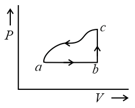
A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process as shown in the figure. The change in the internal energy of the gas along the path is The gas absorbs of heat along the path and along the path . The work done by the gas along the path is:
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
An ideal monoatomic gas occupies a volume of at a pressure of The energy of the gas is:
