The string in the figure shown below has lenth , has a ball attached to one end, and is fixed at its other end. The distance from the fixed end to a fixed peg at point is . When the initially stationary ball is released with the string horizontal as shown, it will swing along the dashed arc. What is its speed when it reaches
(a) its lowest point and (b) its highest point after the string catches on the peg?
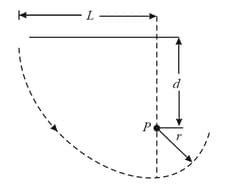
(a) its lowest point and (b) its highest point after the string catches on the peg?


Important Questions on Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
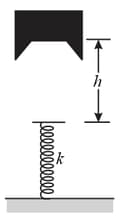
A block of mass is dropped from height onto a spring of spring constant (In the figure shown below). Find the maximum distance the spring is compressed.
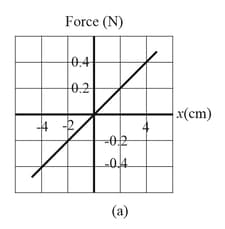
A conservative force where is in meters acts on a particle moving along an axis. The potential energy associated with this force is assigned a value of at
(a) Write an expression for as a function of , with in joules and in meters.
(b) What is the maximum positive potential energy? At what (c) negative value and (d) positive value of is the potential energy equal to zero?
Tarzan, who weighs swings from a cliff at the end of a vine long (In the figure shown below). From the top of the cliff to the bottom of the swing, he descends by . The vine will break if the force on it exceeds . (a) Does the vine break? (b) If it does not, what is the greatest force on it during the swing? If it does, at what angle with the vertical does it break?

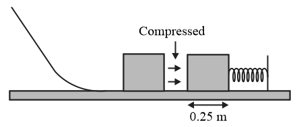
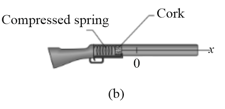
In the figure shown below applies to the spring in a cork gun (In the figure shown below); it shows the spring force as a function of the stretch or compression of the spring. The spring is compressed by and used to propel a cork from the gun.
(a) What is the speed of the cork if it is released as the spring passes through its relaxed position?
(b) Suppose, instead, that the cork sticks to the spring and stretches it before separation occurs. What now is the speed of the cork at the time of release?
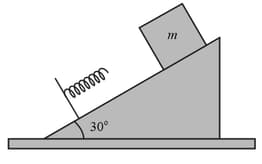
A block moves on a horizontal, frictionless surface and collides with a spring of spring constant that is fixed to a wall. When the block momentarily stops, the spring has been compressed by After rebounding, the block has a speed of . Next, the spring is put on an inclined surface with its lower end fixed in place (In the figure shown below). The same block is now released on the incline at a distance of from the spring's free end. When the block momentarily stops, the spring has been compressed by .
(a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline?
(b) How far does the block then move up the incline from the stopping point?
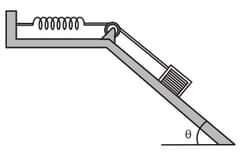
A breadbox on a frictionless incline of angle is connected, by a cord that runs over a pulley, to a light spring of spring constant as shown in the figure shown below. The box is released from rest when the spring is unstretched. Assume that the pulley is massless and frictionless.
(a) What is the speed of the box when it has moved down the incline?
(b) How far down the incline from its point of release does the box slide before momentarily stopping, and what are the
(c) magnitude and (d) direction (up or down the incline) of the box's acceleration at the instant the box momentarily stops?
As shown in the figure shown below, the right end of a spring is fixed to a wall. A block is then pushed against the free end so that the spring is compressed by . After the block is released, it slides along a horizontal floor and (after leaving the spring) up an incline; both floor and incline are frictionless. Its maximum (vertical) height on the incline is . What are (a) the spring constant and (b) the maximum speed? (c) If the angle of the incline is increased, what happens to the maximum (vertical) height?