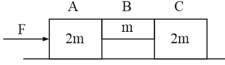
The system is pushed by a force as shown in figure. All surfaces are smooth except between and . Friction coefficient between and is . Minimum value of to prevent block from downward slipping is


Important Questions on Newton's Laws of Motion (With Friction)
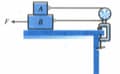
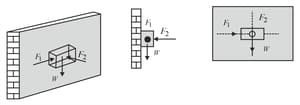
Block , as shown in figure, weighs and block weighs . The coefficient of kinetic friction between all surfaces is . Find the magnitude of the horizontal force necessary to drag block to the left at constant speed if and are connected by a light, flexible cord passing around a fixed, frictionless pulley.
A block of weight is pushed against a rough vertical wall with a force of , coefficient of static friction being . Another horizontal force of , is applied on the block in a direction parallel to the wall. Regarding the situation shown in figure we can say that the block
In the situation shown in figure a wedge of mass is placed on a rough surface, on which a block of equal mass is placed on the inclined plane of wedge. Friction coefficient between plane and the block and the ground and the wedge . An external force is applied horizontally on the wedge. Given that does not slide on incline due to its weight.
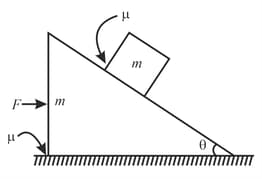
The value of at which wedge will start slipping is:
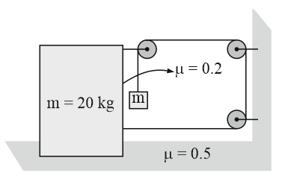
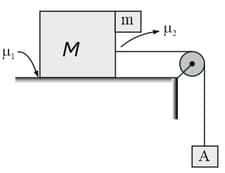
In the arrangement shown in figure, a block of mass is placed on rough horizontal surface with . block of mass is arranged as shown. The maximum value of' in order that system remains in equilibrium:
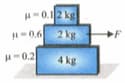
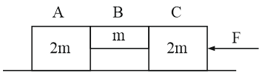
Three blocks and of masses and respectively are arranged as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between different surfaces are shown in figure. A force of magnitude acts on block in horizontal direction. The acceleration of block is
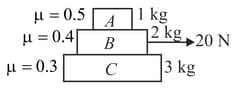
In the situation shown in figure, for what value of force (in Newton) sliding between middle and lower block will start? (Take )