The table shows the number of plants of each species counted in a sand dune.

(a) Calculate the Simpson reciprocal diversity index from the following data for this community, using the formula given below.


Important Questions on Practice Exam Papers
The table shows the number of plants of each species counted in a sand dune.
| Species | Number |
| Sea holly (Acanthus ebracteatus) | 3 |
| Sand couch (Sporobolus virginicus) | 6 |
| Baby grass (Sporobolus pungens) | 1 |
| Total | 10 |
(b) Comment on the richness and evenness of this sand dune community.
The sand dune community was compared with that of a forest where 240 organisms were counted in a total of 10 species. The Simpson diversity index of this forest was 14.
The table shows the number of plants of each species counted in a sand dune.

Distinguish between the biodiversity of the sand dune and the forest studied.
The study of species interactions in urban versus rural environments can improve the understanding of shifts in ecological processes due to urbanization. The leaves of the English oak (Quercus robur) in urban and adjacent rural areas were assessed to determine whether urbanization affected leaf nitrogen content.
Outline two factors in the soil that could affect the nitrogen concentration in leaves of Q. robur.
The graph shows the mean Standard deviation of the nitrogen concentration in leaves of Q. robur growing in urban and rural habitats of large, medium and small cities.
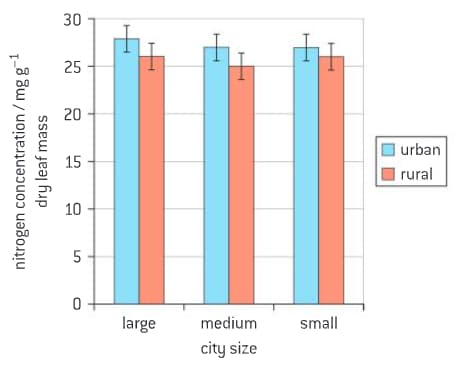
The study of species interactions in urban versus rural environments can improve the understanding of shifts in ecological processes due to urbanization. The leaves of the English oak (Quercus robur) in urban and adjacent rural areas were assessed to determine whether urbanization affected leaf nitrogen content. Describe the effect of city size and urbanization on the Q. robur leaf nitrogen concentration.
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inherited disease that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. It is caused by the deficiency of phenylalanine hydrolase, an enzyme that converts phenylalanine into tyrosine. Treatment is with a diet low in foods that contain phenylalanine and the addition of special supplements.
Serum phenylalanine levels are important indications for proteinrestricted diet therapy. Brain damage might occur if the patient does not follow the diet. The scattergraph shows the incidence of brain damage and the plasma phenylalanine levels of patients who did not stick to the diet.
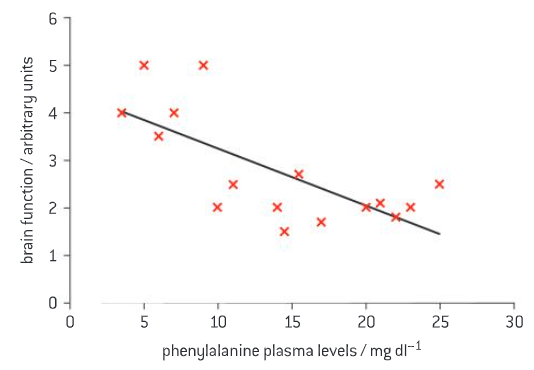
(a) Describe the relationship between phenylalanine plasma levels and brain function.
Orally administered drugs that are not excreted in urine must be completely eliminated by the liver by enzymatic reactions. The rate at which this happens is called the hepatic extraction ratio. A ratio of 1 means all the drug has been removed. Competitive inhibitors bind to the drug but do not catabolize it. The graph shows the relationship between the hepatic extraction ratio and percentage inhibition by a competitive inhibitor.
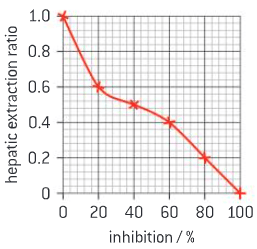
(a) It has been suggested that drug competitive inhibitors can cause drug plasma concentrations to increase, permanently damaging the liver. Discuss this hypothesis using the data provided.
