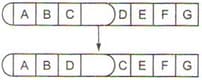
The type of chromosomal aberration indicated in the diagram shows
Important Questions on Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Explain the type of gene mutation in the DNA sequence given below.
ATGCATGC ATGAATGC
I) Pusa swarnim - Brassica - White rust resistance
II) Pusa gaurav - Brassica - Fruit borer resistance
III Pusa sawani - Bhindi - Fruit borer resistance
IV) Pusa sadabahar - Chilli - Leaf curl resistance
Match the following lists:
| List | List | ||
| A) | Change in single base pair of DNA | Recombination | |
| B) | Deletions of base pairs of DNA | Genetic map | |
| C) | Generation of non-parental gene combination | Point mutations | |
| D) | The frequency of recombination between gene pairs on the same chromosome | Frame-shift mutations |
The correct match is
Match the following lists:
| List-I | List-II | ||
| Crop bred by hybridization | Resistance to disease | ||
| (A) | Wheat | (I) | Block rot and curl blight black rot |
| (B) | Brassica | (II) | Mosaic virus, leaf curl |
| (C) | Cauliflower | (III) | Leaf and stripe rust, hill bunt |
| (D) | Cowpea | (IV) | White rust |
| (V) | Bacterial blight |
The correct match is:
Read the following statements and state true (T) and false (F):
A. Deletions and insertions of base pairs of DNA cause frame shift mutations.
B. Classical example of point mutation is sickle cell anaemia.
C. Mendelian disorders are mainly determined by alteration or mutation in a single gene.
D. Haemophilia, colour blindness, and cystic fibrosis are sex-linked recessive disorders.
Read the following statements:
A. The phenomenon which results in alteration of DNA sequence and consequently results in changes in genotype and the phenotype of an organism.
B. In addition to recombination, it is another phenomenon that leads to variation in DNA.
The phenomenon explained above is

