EASY
Earn 100
The variation of kinetic energy (KE) of a particle executing simple harmonic motion with the displacement () starting from mean position to extreme position () is given by
(a)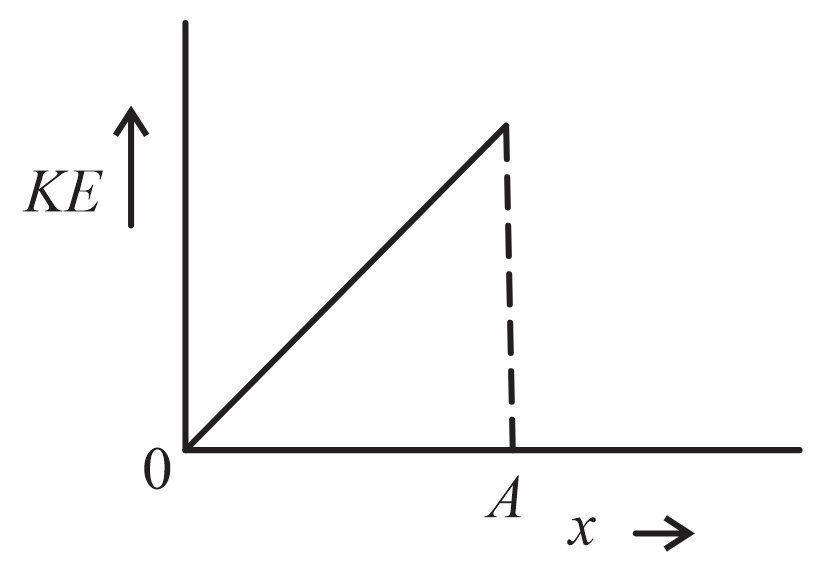
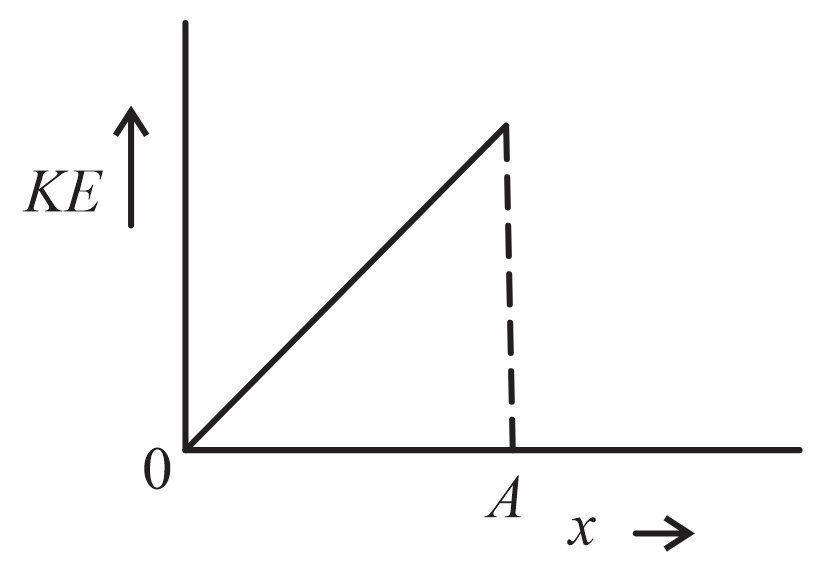
(b)

(c)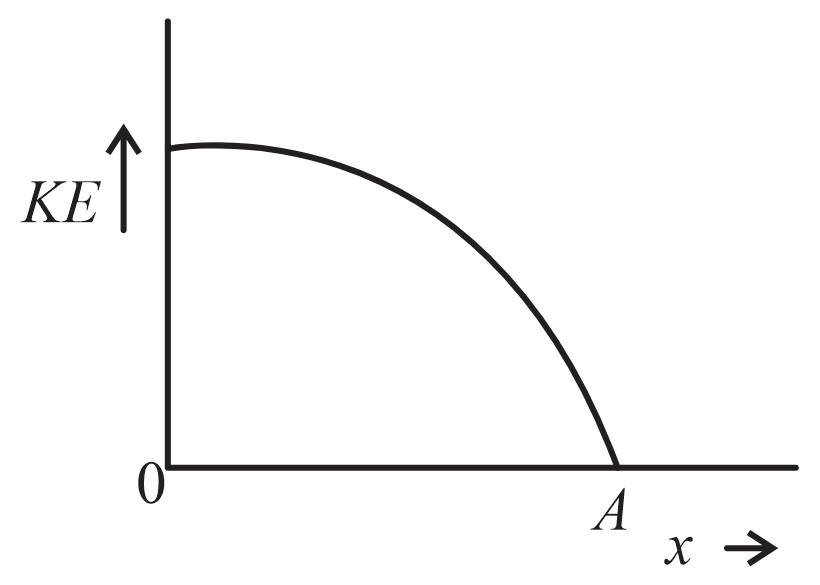

(d)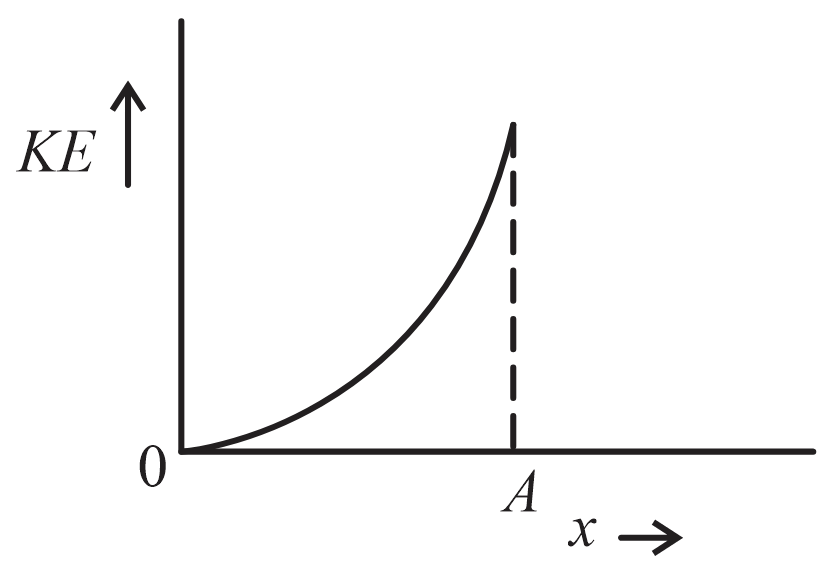

84.91% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Oscillations
HARD
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
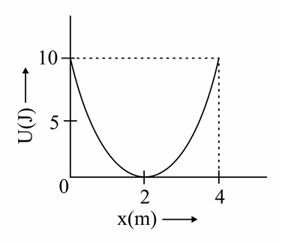
A mass of is connected to a spring. The potential energy curve of the simple harmonic motion executed by the system is shown in the figure. A simple pendulum of length has the same period of oscillation as the spring system. What is the value of acceleration due to gravity on the planet where these experiments are performed ?
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
(a) Potential energy is always equal to its
(b) Average potential and kinetic energy over any given time interval are always equal.
(c) Sum of the kinetic and potential energy at any point of time is constant.
(d) Average in one time period is equal to average potential energy in one time period.
Choose the most appropriate option from the options given below :
HARD
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM

