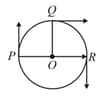
Three point particles , and move in a circle of the radius with different but constant speeds. They start moving at from their initial positions as shown in the figure. The angular velocities (in ) of , and are , and , respectively, in the same sense. The time interval after which they all meet is


Important Questions on Circular Motion
A particle of mass is suspended from a fixed point by a string of length . It is displaced by an angle from the equilibrium position and released from there at . The graph, which shows the variation of the tension in the string with time , maybe:
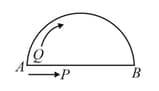
Two particles and start their journey simultaneously from point . moves along a smooth horizontal circular wire with diameter . moves along a curved smooth track. has sufficient velocity at to reach always remaining in contact with the curved track. At , the horizontal component of velocity of is same as the velocity of along the wire. The plane of motion is vertical. If , are times taken by and respectively to reach then (Assume velocity of is constant)
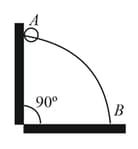
A wire, which passes through the hole is a small bead, is bent in the form of a quarter of a circle. The wire is fixed vertically on the ground as shown in the figure. The bead is released from near the top of the wire, and it slides along the wire without friction. As the bead moves from to , the force it applies on the wire is