Total energy of an isolated system-
Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
A large block of wood of mass is hanging from two long massless cords. A bullet of mass is fired into the block and gets embedded in it. The (block bullet) then swing upwards, their center of mass rising a vertical distance before the (block bullet) pendulum comes momentarily to rest at the end of its arc. The speed of the bullet just before the collision is: (Take )
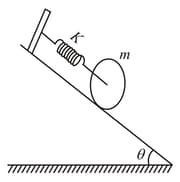
A sphere of mass is attached to a spring of spring constant and is held in unstretched position over an inclined plane as shown in the figure. After letting the sphere go, find the maximum length by which the spring extends, given the sphere only rolls.
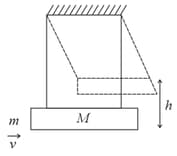
A mass of falls from a height of and lands on a mass less platform supported by a spring having spring constant as shown in the figure. The maximum compression of the spring is.
(acceleration due to gravity )
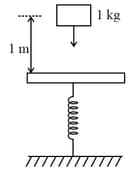
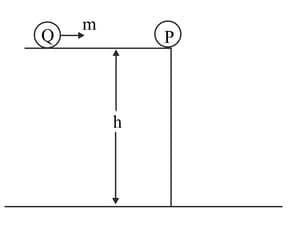
In the given figure, the block of mass is dropped from the point . The expression for kinetic energy of block when it reaches point is
As per the given figure, two blocks each of mass are connected to a spring of spring constant . If both are given velocity in opposite directions, then maximum elongation of the spring is

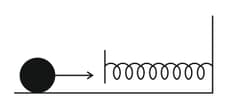
A mass of moving with a speed of on a horizontal smooth surface, collides with a nearly weightless spring of force constant . The maximum compression of the spring would be