HARD
Earn 100
Total number of colourless gases in the given list are
, , , , vapor, , vapor,
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Theoretical Principles of Experimental Chemistry
EASY
In the detection of II group acid radical, the salt containing chloride is treated with concentrated sulphuric acid, the colourless gas is liberated. The name of the gas is
EASY
Reaction of an inorganic sulphite with dilute generated compound . Reaction of with gives . Further, the reaction of with and water affords compound and , respectively, are :
HARD
When a mixture of and concentrated is heated in a dry test tube, a red vapour is evolved. This vapour turns an aqueous solution of yellow due to the formation of and respectively, are:
EASY
The hottest region of Bunsen flame shown in the figure below is:
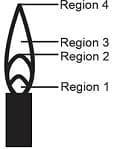
MEDIUM
The sodium salt of an organic acid produces effervescence with concentrated . reacts with the acidified aqueous solution to give a white precipitate which decolourises acidic solution of . is
MEDIUM
Which combines with to form brown complex?
MEDIUM
Sodium nitroprusside, when added to an alkaline solution of sulphide ions, produce a
MEDIUM
A white sodium salt dissolves readily in water to give a solution which is neutral to litmus. When silver nitrate solution is added to the before mentioned solution, a white precipitate is obtained which does not dissolve in dilute nitric acid. The anion is:
EASY
When treated with conc. yields gas which further reacts with to generate a white solid reacts with dil. to produce the same gas the solid is
MEDIUM
and both when dissolved in water containing ions the pair of species formed is:
MEDIUM
The green colour produced in the borax bead test of a chromium(III) salt is due to -
HARD
A white precipitate was formed when was added to water extract of an inorganic salt. Further, a gas with characteristic odour was released when the formed white precipitate was dissolved in dilute HCI. The anion present in the inorganic salt is:
EASY
The blue colour produced when a starch solution is added to a solution containing traces of is due to
(I) formation of
(II) formation of an inclusion complex
(III) Oxidation of starch
(IV) Oxidation of
EASY
On heating, lead (ll) nitrate gives a brown gas (A). The gas (A) on cooling changes to a colourless solid/liquid (B). (B) on heating with NO changes to ablue solid (C). The oxidation number of nitrogen in solid (C) is:
HARD
The reagent(s) that can selectively precipitate from a mixture of and in aqueous solution is (are)
MEDIUM
Match List I with List II.
| List-I (Anion) |
List-II (gas evolved on reaction with dil. ) |
||
| (A) | (I) |
Colourless gas which turns lead acetate paper black. |
|
| (B) | (II) |
Colourless gas which turns acidified potassium dichromate solution green. |
|
| (C) | (III) | Brown fumes which turns acidified KI solution containing starch blue. | |
| (D) | (IV) | Colourless gas evolved with brisk effervescence, which turns lime water milky. |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
HARD
Among the following cases how many will evolve coloured gas or fumes on reaction with concentrated (cold or hot) ?
HARD
Solution of having smell of burnt sulphur
Solution of
blood red colouration
solution of
MEDIUM
Total number of anion(s) which give white precipitate with aqueous solution of is/are:
EASY
When phosphate radical react with ammonium molybdate, the colour of precipitate obtained is

