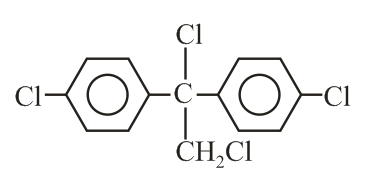
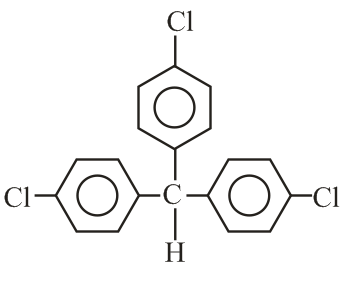
Trichloroacetaldehyde, reacts with chlorobenzene in presence of sulphuric acid and produces
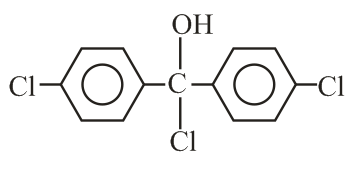
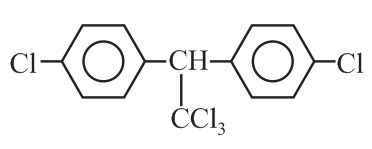

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids from Embibe Experts Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Chemistry Solutions
1. Methods of preparation of carbonyl compounds:
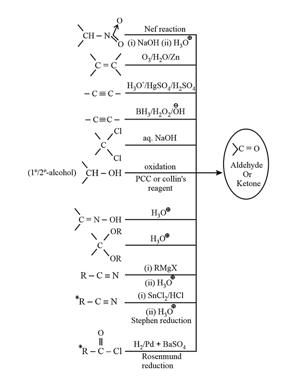
*only used for preparation of aldehyde
2. Chemical properties of carbonyl compounds:
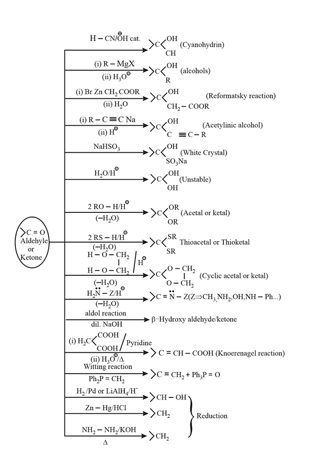
3. Some other important reactions:
(i) Perkin Condensation:
(ii) Beckmann Rearrangement:
The acid catalyzed conversion of ketoximes to -substituted amides is known as Beckmann rearrangement.
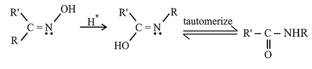
(iii) Cannizzaro’s reaction:
This reaction is preferentially given by those aldehydes which do not contain α-hydrogen. In Cannizzaro reaction, one molecule of the aldehyde is oxidized to acid at the expense of the other which is reduced to alcohol i.e., disproportionation reaction takes place. The reaction occurs in the presence of concentrated solution of any base.
4. Some important points of carbonyl compounds:
(i) Distinction between formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and acetone:
| S.No. | Reagent/Test | |||
|
I. |
Brady reagent/DNP | Colored crystal | Colored crystal | |
|
II. |
Tollen's reagent | Silver mirror | Silver mirror | |
|
III. |
Fehling's solution | Red | Red | |
|
IV. |
Benedict’s solution | Red | Red | |
|
V. |
Black | Black | ||
|
VI. |
Schiff's reagent | Pink | Pink | |
|
VII. |
Iodoform test | yellow | Yellow | |
|
VIII. |
Pyrogallol test | White | ||
|
IX. |
Legal test | Red | Red | |
|
X. |
Blue |
(ii) Chloral is an important intermediate in the manufacture of chloroform and D.D.T.
(iii) Popoff's rule: Oxidation of unsymmetrical ketones largely take place in such a way that the smaller alkyl group remains attached to the group during the formation of two molecules of acids.
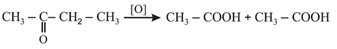
(iv) Formaldehyde is used in preparation of urotropine (Hexamethylenetetramine), a urinary antiseptic and Bakelite (phenol-formaldehyde resin) polymer, throat lozenges (formalin lactose).
(v) Formaldehyde is used as disinfectant and preservative for biological specimens in the form of formalin.
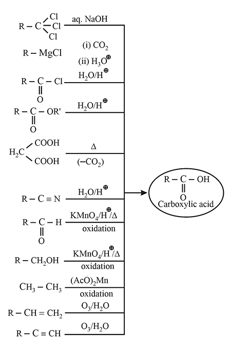
5. Methods of preparation of carboxylic acids:
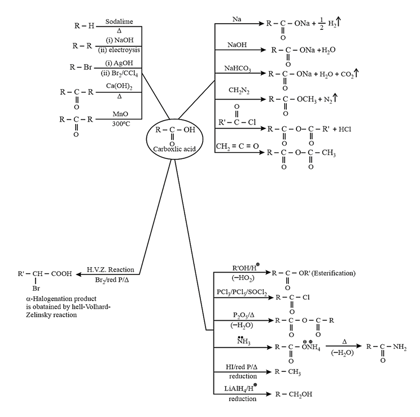
6. Chemical properties of carboxylic acids:
| Heating effect on carboxylic acids | |
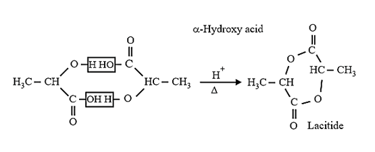 |
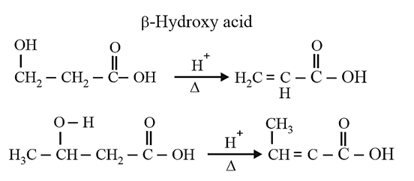 |
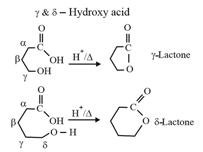 |
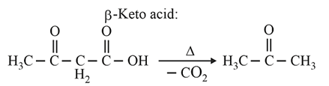 |
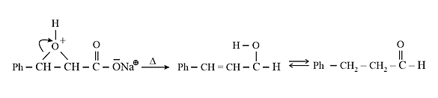 |
7. Carboxylic acid derivatives:
These are formed by the replacement of group of acid by some other
(i) Acid halides:
Chemical Properties:
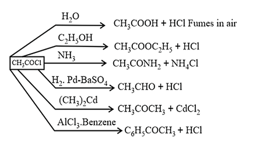
(ii) Acid Anhydrides:
prepared by dehydration of carboxylic acid.
Chemical Properties:
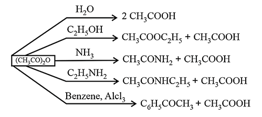
(iii) Esters:
prepared by reaction of acid with alcohol or acid chloride or anhydrides with alcohol.
Chemical Properties:
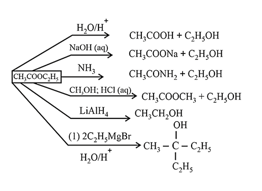
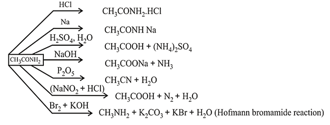
(iv) Acid amides:
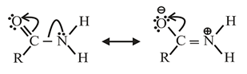
It is prepared by reaction of carboxylic acid or its derivatives with . It is amphoteric in nature. Acid amides act as weak acids as well as weak bases. Lone pair of is delocalized with electrons of
Chemical Properties: