Two conducting rods, when connected between two points at constant but different temperatures separately, the rate of heat flow through them are and .

Important Questions on Calorimetry and Heat Transfer
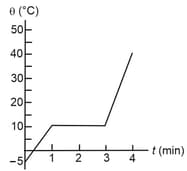
As a physicist, you put heat into a solid sample at the rate of , while recording its temperature as a function of time. You plot your data and obtain the graph shown in figure.
(a) What is the latent heat of fusion for this solid?
(b) What is the specific heat of the solid state of the material?
Three rods of copper, brass and steel are welded together to form a -shaped structure. The cross-sectional area of each rod is . The end of the copper rod is maintained at and the ends of the brass and steel rods at and , respectively. Assume that there is no loss of heat from the surfaces of the rods. The lengths of rods are: copper , brass and steel .
(a) What is the temperature of the junction point?
(b) What is the heat current in the copper rod?
and
.