Two identical bodies are made of a material for which the heat capacity decreases with increase in temperature. One of these is at while the other one is at If the two bodies are brought into contact, then the final common temperature will be-
Important Questions on Thermal Properties of Matter
, where is a constant with appropriate dimension while is a constant with dimension of temperature. The heat capacity of the metal is:
(Specific heat of water is and the density of water is )
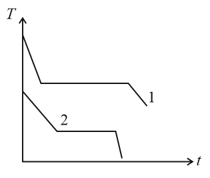
Two different liquids of same mass are kept in two identical vessels, which are placed in a freezer that extracts heat from them at the same rate causing each liquid to transform into a solid. The schematic figure below shows the temperature T vs time t plot for the two materials. We denote the specific heat of materials in the liquid (solid) states to be and respectively.
A horizontal fire hose with a nozzle of cross-sectional area delivers a cubic metre of water in What will be the maximum possible increase in the temperature of water while it hits a rigid wall (neglecting the effect of gravity)?
Due to cold weather, a water pipe of cross-sectional area is filled with ice at Resistive heating is used to melt the ice. Current of is passed through resistance. Assuming that all the heat produced is used for melting, what is the minimum time required?
(Given latent heat of fusion for water/ice specific heat of ice and density of ice

