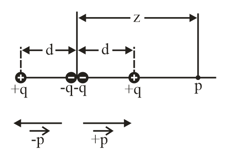
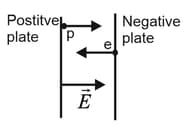
Two large parallel Copper plates are apart and have a uniform electric field between them as depicted in the figure. An electron is released from the negative plate at the same time that a proton is released from the positive plate. Neglect the force of the particles on each other and find their distance from the positive plate when they pass each other. (Does it surprise you that you need not know the electric field to solve this problem?)


Important Questions on Electric Fields
Figure shows an uneven arrangement of electrons and protons on a circular arc of radius, with angles and . What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the axis) of the net electric field produced at the center of the arc?
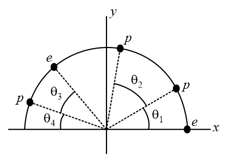
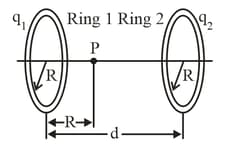
Figure shows two parallel non-conducting rings with their central axes along a common line. Ring has uniform charge and radius , ring has uniform charge and the same radius . The rings are separated by distance, . The net electric field at point on the common line at distance from ring is zero. What is the ratio ?
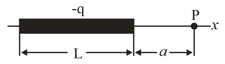
In figure shown below, positive charge, is spread uniformly along a thin non-conducting rod of length, . What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the -axis) of the electric field produced at point at a distance, from the rod along its perpendicular bisector?
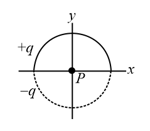
In figure shown below, two curved plastic rods, one of charge and the other of charge form a circle of radius, in an -plane. The -axis passes through both the connecting points and the charge is distributed uniformly on both rods. If , what are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the -axis) of the electric field produced at at the center of the circle?
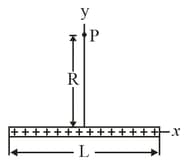
In the figure, a non-conducting rod of length, has a charge, uniformly distributed along its length. (a) What is the linear charge density of the rod? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction (relative to the positive direction of the -axis) of the electric field produced at point at a distance, from the rod? What is the electric field produced at distance, by (d) the rod and (e) a particle of charge, that we use to replace the rod? (At that distance, the rod looks like a particle.)
In figure, a thin glass rod forms a semicircle of radius Charge is uniformly distributed along the rod with in the upper half and in the lower half. What are the magnitude and direction (relative to the positive direction of the -axis) of the electric field at the center of the semicircle?
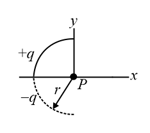
Figure shows a generic electric quadrupole. It consists of two dipoles with dipole moments that are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. Show that the value of on the axis of the quadrupole for a point at a distance from its center (assume ) is given by, in which is known as the quadrupole moment of the charge distribution.