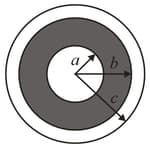
Two long, charged, thin-walled, concentric cylindrical shells have radii of and . The charge per unit length is on the inner shell and on the outer shell. What is the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (radially inward or outward) of the electric field at radial distance ? What is (c) and (d) the direction at ?

Important Questions on Gauss' Law
The figure shows a spherical shell with uniform volume charge density , inner radius , and outer radius . What is the magnitude of the electric field at radial distances (a) , (b) , (c) , (d) , (e) and (f) ?
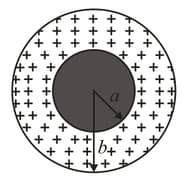
In the figure shown below, a solid sphere of radius is concentric with a spherical conducting shell of inner radius and outer radius . The sphere has a net uniform charge ; the shell has a net charge . What is the magnitude of the electric field at radial distances (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) and (f) What is the net charge on the (g) inner and (h) outer surface of the shell?
In the fig. a butterfly net is in a uniform electric field of magnitude . The rim, a circle of radius is aligned perpendicular to the field. The net contains no net charge. Find the electric flux through the net.
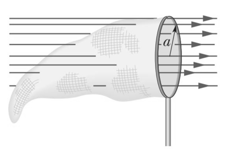
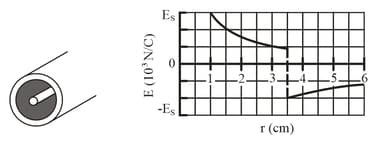
Figure (a) shows a narrow charged solid cylinder that is coaxial with a larger charged cylindrical shell. Both are non-conducting and thin and have uniform surface charge densities on their outer surfaces. Figure (b) gives the radial component of the electric field versus radial distance from the common axis, and What is the shell's linear charge density?
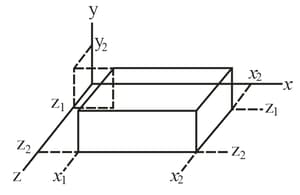
The box-like Gaussian surface shown in the fig. encloses a net charge of and lies in an electric field given by with and in meters and a constant. The bottom face is in the plane; the top face is in the horizontal plane passing through . For and what is the value of