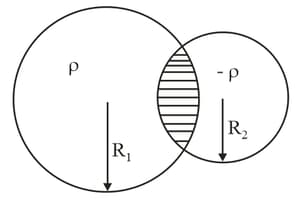
Two non-conducting spheres of radii and and carrying uniform volume charge densities and respectively, are placed such that they partially overlap, as shown in the figure. At all points in the overlapping region :


Important Questions on Electrostatics
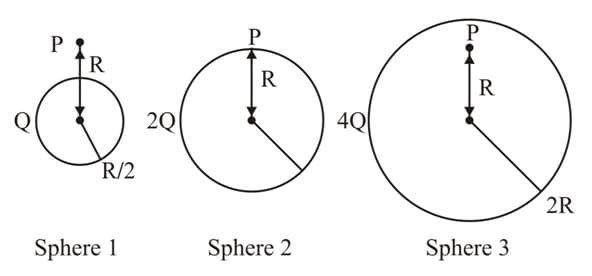
Charges and are uniformly distributed in three dielectric solid spheres and of radii and respectively, as shown in figure. If magnitudes of the electric fields at point at a distance from the centre of spheres and are and respectively, then :-
Assertion : A point charge a is placed at centre of spherical cavity inside a spherical conductor as shown. Another point charge is placed outside the conductor as shown. Now as the point charge is pushed away from conductor, the potential difference between two points and within the cavity of sphere remains constant.
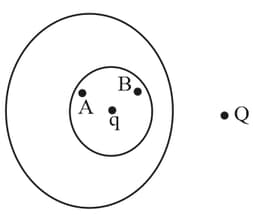
Reason : The electric field due to charges on outer surface of conductor and outside the conductor is zero at all points inside the conductor.
Assertion: A solid uncharged conducting cylinder moves with acceleration (w.r.t ground). As a result of the acceleration of the cylinder, an electric field is produced within a cylinder.
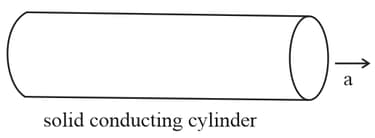
Reason: When a solid conductor moves with acceleration a then from a frame of conductor a pseudo force (of magnitude where is mass of electron) will act on free electrons in the conductor. As a result, some portion of the surface of the conductor acquires a negative charge and a remaining portion of a surface of conductor acquires a positive charge.
Assertion: Two concentric conducting spherical shells are charged. The charge on the outer shell is Varied keeping the charge on the inner shell constant, as a result, the electric potential difference between the two shells does not change.
Reason: If the charge is changed on a thin conducting spherical shell, the potential at all points inside the shell changes by the same amount.
Assertion: The electric potential and the electric field intensity at the centre of a square having four point charges at their vertices (as shown) are zero.
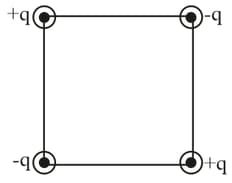
Reason: Electric field is a negative derivative of the potential.
Assertion: No two electric lines of force can intersect each other.
Reason: Tangent at any point of electric line of force gives the direction of electric field.
Assertion : Positive charge always moves from a higher potential point to a lower potential point.
Reason : Electric potential is a vector quantity.
Assertion: On going away from a point charge or a small electric dipole, the electric field decreases at the same rate in both cases.
Reason: Electric field is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the charge in all cases.
