Two smooth spheres of the same radius, but which have different massescollide inelastically. Their velocities before collision are respectively along the directions shown in the figure in which An observer moving parallel to the positive y - axis with a constant speed of observes this collision. He finds the final velocity of to be along the y - direction and the total loss in the kinetic energy of the system to be of its initial value. Determine;
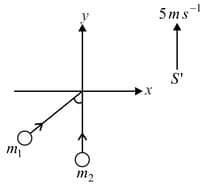
The ratio of the masses
The velocity of after collision with (respect to observer)


Important Questions on Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions
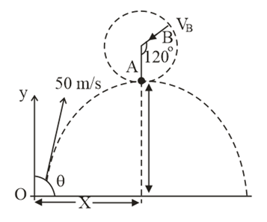
A bullet of mass is fired with a velocity at an angle with the horizontal. At the highest point of its trajectory, it collides head on with a bob of mass suspended by a massless rod of length and gets embedded in the bob. After the collision, the rod moves through an angle Find
The angle of projection.
The vertical and horizontal coordinates of the initial position of the bob with respect to the point of firing of the bullet.
A steel ball falling vertically strikes a fixed rigid plate A with velocityand rebounds horizontally. The ball then strikes a second fixed rigid plate B and rebounds vertically as shown. Assuming smooth surface and the effect of gravity on motion of ball is to be neglected. Determine
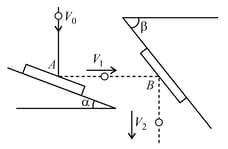
The required angles
The magnitude of the velocity Consider coefficient of restitution for both plates as
Two skaters each of massare approaching each another on a frictionless surface, each with a speed of Skater A carries a ball of mass Both skaters can toss the ball at relative to themselves such that when tosses the ball at to then the ball leaves at with respect to the ground. Further, they start tossing the ball back and forth when they are apart Assume that the motion is one dimensional, all collisions are completely inelastic and that the time delay between receiving the ball and tossing it back is
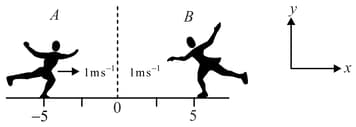
State initial momenta of skaters (just before ).
At skater tosses the ball to skater State momenta of both the skaters immediately after catches the ball.
Indicates the minimum number of tosses by each skater required to avoid collision.
Number of tosses by Number of tosses by
(d) Indicate motion of each skater on the following if no tosses are made. [Note : For this and next part you must select the scale on the time axis approximately. You may use a pencil for sketching].
Indicate motion of each skater on the following from till just after one round trip by the ball (from A to B and back to A).
This problem is designed to illustrate the advantage that can be obtained by the use of multiple-staged instead of single-staged rockets as launching vehicles. Suppose that the payload (e.g., a space capsule) has mass and is mounted on a two-stage rocket (see figure). The total mass (both rockets fully fuelled, plus the payload) is
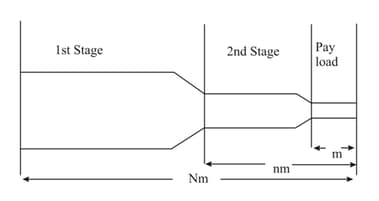
The mass of the second-stage rocket plus the payload, after first-stage burnout and separation, is . In each stage the ratio of container mass to initial mass (container plus fuel) is and the exhaust speed is constant relative to the engine. Note that at the end of each state when the fuel is completely exhausted, the container drops off immediately without affecting the velocity of rocket. Ignore gravity.
Obtain the velocity of the rocket gained from the first-stage burn, starting from rest in terms of
Obtain a corresponding expression for the additional velocity gained from the second stage burn.
Adding, you have the payload velocity in terms of Taking and as constants, find the value of for which is a maximum. For this maximum condition obtain
Find an expression for the payload velocity of a single-stage rocket with the same values of
Suppose that it is desired to obtain a payload velocity of using rockets which and . Using the maximum condition of part obtain the value of if the job is to be done with a two-stage rocket.
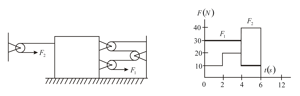
The block is moving to the right with a speed of when it is acted upon by the forces and . These forces vary in the manner shown in the graph. Find the velocity (in ) of the block at . Neglect friction and masses of the pulleys and cords.
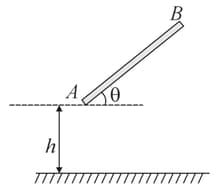
A uniform rod of length is released from rest with inclined at angle with horizontal. It collides elastically with smooth horizontal surface after falling through a height . What is the height upto which the centre of mass of the rod rebounds after impact?