Water and bromine are both simple molecular substances.
The boiling point of water is 100°C. The boiling point of bromine is 59°C. Explain the reason for this difference in terms of intermolecular forces.

Important Questions on States of Matter
Use ideas about the kinetic theory to explain what happens when liquid bromine evaporates to form bromine vapour.
When 0.20 g of a liquid, Y, with a simple molecular structure was evaporated it produced 80 cm3 of vapour.
The temperature was 98 °C and the pressure 1.1 × 105 Pa. Calculate the relative molecular mass of Y.
(R = 8.31 JK–1mol–1)
The uses of metals are often related to their properties.
Describe the structure of a typical metal.
Explain why metals are malleable.
The uses of metals are often related to their properties.
Use the information in the table below to answer the question that follows:
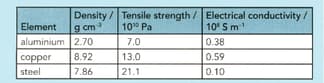
Why is aluminium more suitable than steel for building aeroplane bodies?
The uses of metals are often related to their properties.
Use the information in the table below to answer the question that follows:
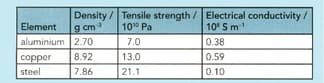
Explain why overhead electricity cables are made from aluminium with a steel core rather than just from copper.
The uses of metals are often related to their properties.
The effect of alloying copper with zinc on the strength of the alloy is shown in the table below.
| % copper | % zinc | Tensile strength / 108 Pa |
| 100 | 0 | 2.3 |
| 80 | 20 | 3.0 |
| 60 | 40 | 3.6 |
| 0 | 100 | 1.4 |
Describe and explain the change in tensile strength as the percentage of zinc increases from 0% to 40%.
The diagram shows the structures of graphite and diamond.
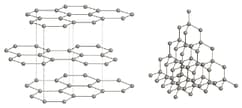
Use the diagrams and your knowledge of structure and bonding to answer the following question.
Explain why both diamond and graphite have high melting points.
