EASY
Earn 100
We connect a charge capacitor to an inductor the electric current and charge on the capacitor in the circuit undergoes LC oscillations.
(a)True
(b)False
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Alternating Current
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
If the instantaneous emf and the instantaneous current equations of an A.C. circuit are respectively.
then the phase difference between voltage and current is :
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
If a student plots graphs of the square of maximum charge on the capacitor with time (t) for two different values and of L then which of the following represents this graph correctly? (plots are schematic and not drawn to scale)
MEDIUM
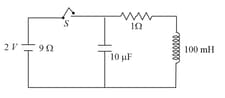
At a certain moment, the switch shown in the figure is disconnected. The energy of the oscillations immediately after the switch is disconnected and at time from the time switch is disconnected are, respectively
HARD
HARD
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
EASY

