What are afferent nerves and efferent nerves?
Important Questions on Neural control and Coordination
Name the following:
Receptors that detect taste.
Name four plant hormones.
Give one term for the following:
Receptors responsible for taste.
Name one gustatory receptor and one olfactory receptor present in human beings.
i) David and Debbie were riding a bike without helmets and met with an accident.
Observe the diagram of the human brain and identify the part of the brain marked A, B or C affected in the following cases.
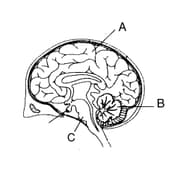
a) Debbie had an instant death.
b) David lost all his memory and ability to think.
Write a and b in the given flow chart of neuron through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
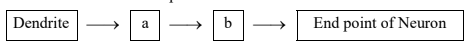
Select the most correct alternative from those given below each statement and write the completed statement:
The thinking part of the brain is the _____.
Give one term for the following:
The gap between two neurons.
Analyse the illustration and answer the following questions :
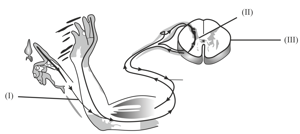
Write the names of (i) and (ii).

