What is Snell's Window?
Important Questions on Ray Optics
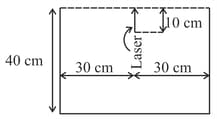
A water-proof laser pointer of length placed in a water tank rotates about a horizontal axis passing through its centre of mass in a vertical plane as shown in the figure. The time period of rotation is 60 s. Assuming the water to be still and no reflections from the surface of the tank, the duration for which the light beam escapes the tank in one time period is close to (Take, refractive index of water )
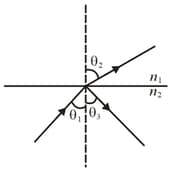
A monochromatic beam of light is incident at the interface of two materials of refractive index and as shown. If and is the critical angle then which of the following statement is true?
(refractive index of fiber is , and .)
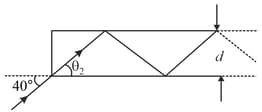
A right-angled isosceles prism is held on the surface of a liquid composed of miscible solvents and of refractive index and respectively. The refractive index of prism is and that of the liquid is given by where is the percentage of solvent in the liquid:-
If is the critical angle at prism-liquid interface, the plot which best represents the variation of the critical angle with the percentage of solvent is:
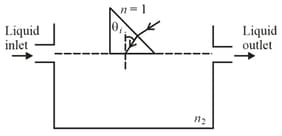
Light guidance in an optical fiber can be understood by considering a structure comprising of thin solid glass cylinder of refractive index surrounded by a medium of lower refractive index . The light guidance in the structure takes place due to successive total internal reflections at the interface of the media and as shown in the figure. All rays with the angle of incidence less than a particular value are confined in the medium of refractive index . The numerical aperture (NA) of the structure is defined as .
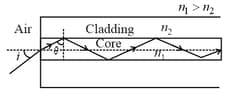
For two structures namely with and , and with and and taking the refractive index of water to be and that of air to be 1, the correct option(s) is (are)
[Speed of light
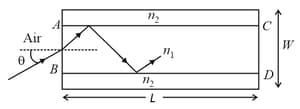
Light guidance in an optical fiber can be understood by considering a structure comprising of thin solid glass cylinder of refractive index surrounded by a medium of lower refractive index . The light guidance in the structure takes place due to successive total internal reflections at the interface of the media and as shown in the figure. All rays with the angle of incidence less than a particular value are confined in the medium of refractive index . The numerical aperture (NA) of the structure is defined as .

If two structures of same cross-sectional area, but different numerical apertures and are joined longitudinally, the numerical aperture of the combined structure is

