EASY
Earn 100
What is XL and XC?
Important Questions on Alternating Current
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
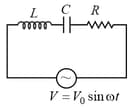
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
HARD
An AC voltmeter connected between points and in the circuit below reads If it is connected between and the reading is The reading when it is connected between and is . What will the voltmeter read when it is connected between and ( Assume that the voltmeter reads true RMS voltage values and that the source generated a pure AC.)
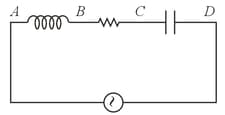
HARD
If the input voltage to the circuit below is given by the output voltage is given by .
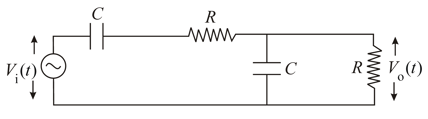
Which one of the following four graphs best depict the variation of vs ?
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
i. When capacitor is air filled.
ii. When capacitor is mica filled.
Current through resistor is and voltage across capacitor is then:
EASY
EASY

