EASY
Earn 100
What is linear magnification?
Important Questions on Reflection of Light
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
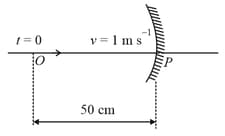
A point object is moving uniformly towards the pole of a concave mirror of focal length along its axis as shown below. The speed of the object is . At , the distance of the object from the mirror is . The average velocity of the image formed by the mirror between time and is:
EASY
MEDIUM
| Column 1 | Column 2 | ||
| (A) | (a) | Convex mirror | |
| (B) | (b) | Concave mirror | |
| (C) | (c) | Real image | |
| (D) | (d) | Virtual image |
EASY
MEDIUM
| Object pin | Convex Lens | Convex Mirror | Image Pin |
| 22.2 cm | 32.2 cm | 45.8 cm | 71.2 cm |
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
Reason: Laws of reflection are strictly valid for plane surfaces, but not for large spherical surfaces.
MEDIUM
EASY
Reason: A convex mirror has a much larger field of view than a plane mirror or a concave mirror.
EASY
EASY
Reason:
HARD
The distance of an object from a spherical mirror is equal to the focal length of the mirror. Then the image :

