EASY
Earn 100
What is the difference between microsporangia and microsporangium?
Important Questions on Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
EASY
Pollen grains are well-preserved as fossils because of the presence of _____.
HARD
Why meiosis is essential at the time of sporogenesis in angiosperms? Explain the process of formation of male gametophyte in angiosperms with suitable diagrams.
HARD
Observe the diagram of the young anther given below:
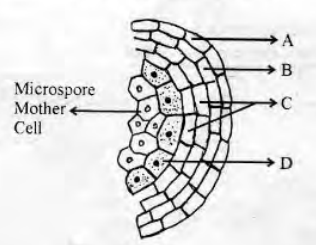
Identify the parts labelled as A, B, C and D.
HARD
Which one of the following statements is not true?
HARD
Mateh the following?
| Column - I | Column - II | Column - III | |||
| (a) | Epidermis | (i) | Multi nucleated | (p) | Protection |
| (b) | Endothecium | (ii) | Homogenous | (q) | Formation of Micropores |
| (c) | Tapetum | (iii) | One celled thick | (r) | dehiscence of anther |
| (d) | Sporogenous tissue | (iv) | Fibrous thickness | (s) | Nourishment |
HARD
Which of the following has proved helpful in preserving pollen as fossils?
HARD
Describe the structure of a typical angiospermic microsporangium with a diagram. Also, explain the function of each part.
EASY
Ubisch bodies are produced from ___.
EASY
The hard outer layer of pollens, named exine, is made of
MEDIUM
Where are the sporopollenin present in the male gametophyte of an angiosperm? Mention the function of it.
EASY
Male gametophyte in angiosperms produces :
MEDIUM
Choose the correct statement.
A) Several hormonal and structural changes are initiated for the development of floral primordium.
B) Each anther will have two sporangia at the sides.
C) Stomium will be useful for the dehiscence of pollen sacs.
D) Pollen grains can be stored at .
E) Pollen viability in rice will be days.
EASY
Which one of the following statements is not true?
HARD
With the help of a well-labelled diagram, describe the development of a male gametophyte of an angiosperm. What is sporopollenin.
EASY
Pollen tablets are available in the market for:
EASY
During an excavation of soil, pollen fossil were retrieved from deepest layer of soil. The pollen grains remained fossils because:
EASY
If we explore anther wall from outside to inside then which sequence will be correct?
A- Endothecium
B- Tapetum
C- Epidermis
D- Middle Layer
EASY
Where are the germ pore present in the male gametophyte of an angiosperm? Mention the function of it.
MEDIUM
Arrange the sequence of events in microsporogenesis.
(A) Disassociation of microspore as pollen grains
(B) Anther maturation and dehydration
(C) Pollen mother cell undergoes meiotic division
(D) Microspore tetrad
EASY
In Angiosperms, microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis:

