EASY
Earn 100
What type of intermolecular forces exist between and ?
(a)Dispersion forces
(b)Dipole-dipole forces
(c)Dipole-induced dipole forces and dispersion forces
(d)Dispersion and dipole-dipole forces
100% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on States of Matter: Gaseous and Liquid States
MEDIUM
In which of the following solid substance dispersion forces exist?
EASY
EASY
[ is the distance between the polar molecules]
EASY
(Latent heat of ice is and )
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
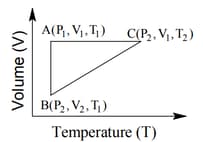
The correct option(s) is (are)
MEDIUM
Match the type of interaction in column with the distance dependence of their interaction energy in column
| A | B |
| (i) ion - ion | (a) |
| (ii) Dipole - dipole | (b) |
| (iii) London dispersion | (c) |
| (d) |
EASY
Increasing order of boiling points in the following compounds is:
MEDIUM
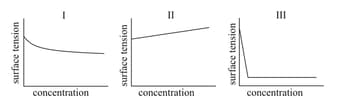
EASY
HARD
HARD
MEDIUM
The combination of plots which does not represent isothermal expansion of an ideal gas is
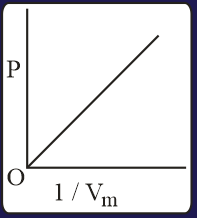
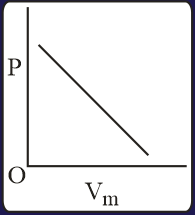
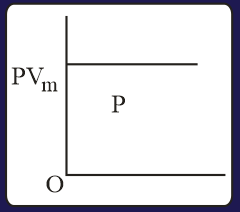
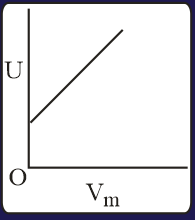
MEDIUM
(R = 8.314 J/mol K) (ln7.5 = 2.01)
HARD
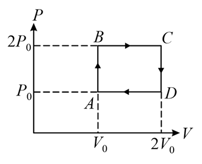
The above diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono-atomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle, is:
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY

