MEDIUM
Earn 100
What will be the molecular formula of a polypeptide consisting of 10 glycine residues?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Biomolecules
EASY
MEDIUM
Explain essential and non-essential amino acid with example.
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
i. Cysteine can be linked to tyrosine by S-O bond.
ii. Cysteine can be linked to another cysteine by S-S bond.
iii. Cysteine can complex with
iv. Cysteine can be linked to methionine by S-S bond
HARD
HARD
A small viral peptide can insert its amino acids (represented as a barrel) into the lipid bilayer as depicted in the figure given below.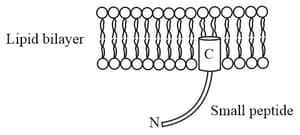
The table depicts the different properties of amino acids.
| Properties | |||
| Polar and uncharged | Polar and charged | Non-polar and hydrophobic | |
| Amino acids | Gly | Asp | Ala |
| Ser | Glu | Val | |
| Thr | Lys | Leu | |
| Cys | Arg | Ile | |
| Asn | His | Pro | |
| Gln | - | Met | |
| Tyr | - | Phe | |
| - | - | Trp | |
EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
Match the following
| (a) | Inhibitor of catalytic activity | (i) | Ricin |
| (b) | Possess peptide bonds | (ii) | Malonate |
| (c) | Cell wall material in fungi | (iii) | Chitin |
| (d) | Secondary metabolite | (iv) | Collagen |
Choose the correct option from the following
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY

