EASY
Earn 100
Which of the following options correctly represent the sign of work done by applied force and gravitational force respectively when a body is raised through height from the surface of Earth ?
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Laws of Motion
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
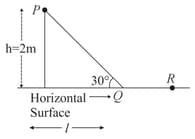
The values of the coefficient of friction and the distance , are respectively close to:
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
Assertion : The work done by the electrostatic force is zero when a point charge moves in a circular path around another charge.
Reason : The dot product of force and displacement vectors gives work done.
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
A block of mass slides from rest at a height on a frictionless inclined plane as shown in the figure. It travels a distance across a rough horizontal surface with coefficient of kinetic friction and compresses a spring of spring constant by a distance before coming to rest momentarily. Then the spring extends and the block travels back attaining a final height of .
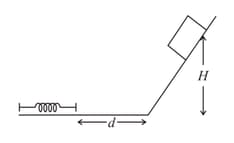
Then
MEDIUM
F = ax + bx2 where a and b are constants. The work done in stretching the unstretched rubber-band by L is :
HARD