EASY
Earn 100
Which of the following phenomenon confirms transverse nature of electromagnetic waves?
(a)Refraction of light.
(b)Diffraction of light.
(c)Dispersion of light.
(d)Polarization of light.
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Wave Optics
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
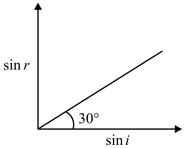
A transparent medium shows relation and as shown. If the speed of light in vacuum is the Brewster angle for the medium is
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
Unpolarised red light is incident on the surface of a lake at incident angle . An observer seeing the light reflected from the water surface through a polariser notices that on rotating the polariser, the intensity of light drops to zero at a certain orientation. The red light is replaced by unpolarised blue light. The observer sees the same effect with reflected blue light at incident angle .
Then,
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY

