Write down the wave equation and use it to estimate the wavelength of ripples on the surface of a pond.

Important Questions on Stationary Waves
A stationary (standing) wave is set up on a vibrating spring. Adjacent nodes are separated by . Calculate:
(a) The wavelength of the progressive wave
A stationary (standing) wave is set up on a vibrating spring. Adjacent nodes are separated by . Calculate the distance from a node to an adjacent anti node.
Look at the stationary (standing) wave on the string in Figure. The length of the vibrating section of the string is 60cm.
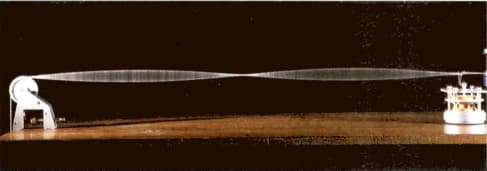
The frequency of vibration is increased until a stationary wave with three antinodes appears on the string.
(a) Determine the wavelength of the progressive wave and the separation of the two neighbouring antinodes.
Look at the stationary (standing) wave on the string in Figure. The length of the vibrating section of the string is 60cm.
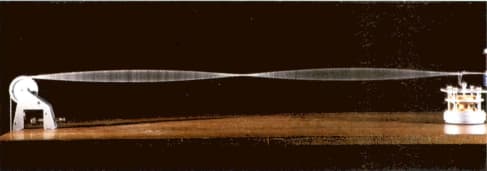
(b) Sketch a stationary wave pattern to illustrate the appearance of the string.
Look at the stationary (standing) wave on the string in Figure. The length of the vibrating section of the string is 60cm.
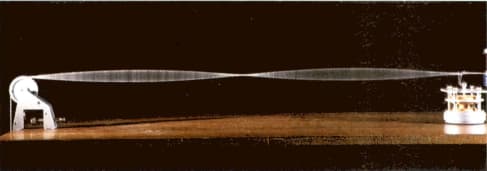
(c) Calculate the wavelength of the progressive wave on this string.
(a) For the arrangement shown in Figure suggest why it is easier to determine accurately the position of a node rather than an antinode.
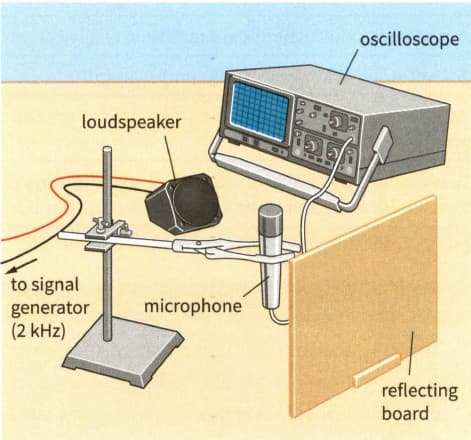
A stationary sound wave is established between the loudspeaker and the board.
For sound waves of frequency , it is found that two nodes are separated by , with three antinodes between them.
(a) Determine the wavelength of these sound waves.
