Write the word equation for the reaction of caesium with water.

Important Questions on Patterns and Properties of Metals
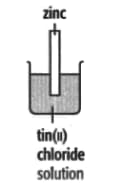
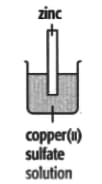
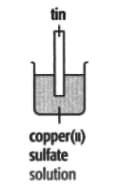
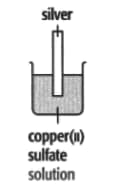
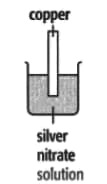
In each of the experiments below, a piece of metal is placed in a solution of a metal salt. Complete the table of observations.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| At start | Colour of metal | grey | _____ | silver-coloured | silver-coloured | _____ |
| Colour of solution | colourless | _____ | blue | blue | colourless | |
| At finish | Colour of metal | coated with silver coloured crystals | _____ | coated with brown solid | silver-coloured | coated with silver-coloured crystals |
| Colour of solution | colourless | _____ | colourless | blue | _____ | |
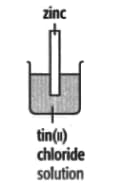
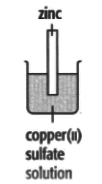
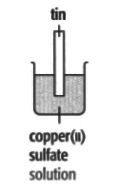
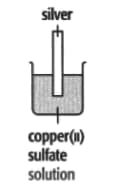
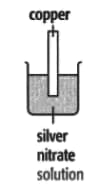
In each of the experiments below, a piece of metal is placed in a solution of a metal salt. The observation table is shown below:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| At start | Colour of metal | grey | grey | silver-coloured | silver-coloured | brown |
| Colour of solution | colourless | blue | blue | blue | colourless | |
| At finish | Colour of metal | Coated with silver coloured crystals | Coated with brown solid | Coated with brown solid | silver-coloured | Coated with silver-coloured crystals |
| Colour of solution | colourless | colourless | colourless | blue | blue | |
Use these results to place the metals copper, silver, tin and zinc in order of the reactivity (putting the most reactive metal first).
In the metal displacement reactions, the atoms of the reactive metal lose electrons to become ions. For example:
Is this reduction or oxidation?
The table shows some properties of a selection of pure metals.
| Metal | Relative abundance in Earth's crust | Cost of extraction | Density | Strength | Melting Point | Electrical conductivity relative to iron |
| Iron | low | high | high | |||
| Titanium | very high | low | high | |||
| Aluminum | high | low | medium | |||
| Zinc | low | high | low | |||
| Copper | low | high | medium | |||
| Tin | low | high | low | |||
| Lead | low | very high | low |
Use information from the table to answer the following question:
Why is aluminium used for overhead power cables?
The table shows some properties of a selection of pure metals.
| Metal | Relative abundance in Earth's crust | Cost of extraction | Density | Strength | Melting Point | Electrical conductivity relative to iron |
| Iron | low | high | high | |||
| Titanium | very high | low | high | |||
| Aluminum | high | low | medium | |||
| Zinc | low | high | low | |||
| Copper | low | high | medium | |||
| Tin | low | high | low | |||
| Lead | low | very high | low |
Use information from the table to answer the following question:
Why do the aluminium cables have an iron (or steel) core?
