Process of Recombinant DNA Technology
Process of Recombinant DNA Technology: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Recombinant DNA Technology, Tools of Recombinant DNA Technology, Enzymes Used in Recombinant DNA Technology, Lysing Enzymes, Cleaving Enzymes, Synthesizing Enzymes, Restriction Enzymes, etc.
Important Questions on Process of Recombinant DNA Technology
Choose the option that is showing the correct sequence of events occurring in each cycle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
A recombinant DNA is formed when sticky ends of vector DNA and foreign DNA join. The sticky ends are formed by which of the following enzymes:
Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation described as natured genetic engineering is used to resist plants from:
Which of the following technique is used for separating the fragments of DNA cut by restriction endonucleases?
Biotechnologists refer to which of the following bacteria as a natural genetic engineer of plants.
Which of the following feature of a vector is required to identify the transformed cell?
In recombinant DNA technology, ‘molecular scissors’ are:
The source organisms that possess Taq polymerase are
An extra-chromosomal, self-replicating part of the cell that has proven to be a boon to biotechnology is:
In which of the following technique the bacterium Thermus aquatics is used:
Colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to non-recombinant bacteria because of
The genes (a) ori, (b) ampR and (c) rop are associated with which of the following vectors:
Fragments of DNA segments can be separated by:
In genetic engineering, which of the following is used?
In four separate experiments (Table), a vector and a fragment was digested with the indicated restriction enzymes. Both, the digested vector and were purified and ligated. represents the ampicillin resistant gene and Ori is the origin of replication. The resultant recombinant vector was transformed into Escherichia coli cells and incubated in a liquid nutrient medium with ampicillin for hours at . Based on the restriction enzymes used for cloning, choose the correct option.
| Experiment No. | Restriction enzymes used |
| 1 | BamHI and SalI |
| 2 | EcoRI and SalI |
| 3 | KpnI and HindIII |
| 4 | KpnI and SalI |
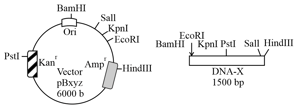
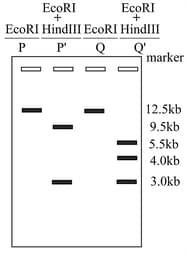
A pure culture of Escherichia coli was streaked on a plate to get single isolated colonies. The plasmid DNA from two such colonies was individually isolated. The DNA were then individually treated with ( and ) or double digested with (and ). The digested DNA were electrophoresed on an agarose gel and the pattern of the linear DNA so obtained is depicted in the figure below. Patterns and are obtained for DNA from colony and are as expected for the original DNA sequence of the plasmid. The best reason for the differing pattern in is because the plasmid DNA from colony has a mutation
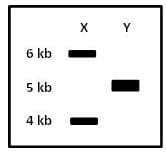
As indicated in the gel image, lanes and represent samples obtained from a circular plasmid after complete digestion using restriction enzyme or with different recognition sites, respectively. How many sites for and are present in the plasmid (sizes of the bands in kilo base pairs is shown)?
Bacterial plasmids are genetic entities that
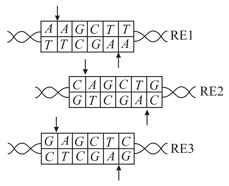
Provided below are recognition sequences for restriction enzymes and Arrows indicate the positions where the enzymes digest on the two strands. Which of the following can the digested DNA ligate to?
Exonuclease is an enzyme that
