Chemical Analysis of Organic Compounds
Chemical Analysis of Organic Compounds: Overview
This topic sheds light on the chemical analysis of organic compounds through various methods. It briefs on acid-soluble fraction and acid-insoluble fraction. It also discusses the compounds which are found in the acid-insoluble fraction.
Important Questions on Chemical Analysis of Organic Compounds
For chemical analysis of living tissue, it is ground in _____ using a mortar and pestle.
Acid insoluble fraction does NOT contain
Living cell contains water. Water present in human body is
_____ of total cell mass is formed by ions.
The percentage of oxygen in human body is
When the dry tissue is burnt, the ash is obtained, which contains
The amount of which of the element is greatest in protoplasm?
The type of bond involved in the formation of sodium chloride is
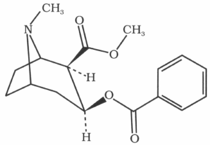
Which plant has a chemical compound whose structure is given below?
Arrange the following elements in the descending order in terms of percentage weight of human body.
During the elemental analysis of tissue, if the tissue is fully burnt, all the carbon compounds are oxidized to gaseous form and the remaining is called ash. This ash contains which of the following?
Which acid is used in the chemical analysis of living tissue?
The most abundant intracellular cation is
The acid used in separating biomolecules is
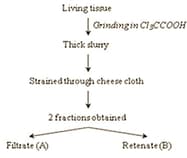
Given below is the process to separate the contents of a living tissue by acid treatment and a list of certain observations. Segregate the observations under filtrate(A) and retentate(B) and select the correct combination.
Molecular weight ranging from 18-800 daltons approx.
Proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides and lipids
Chemicals more than 800 daltons molecular weight
Has monomeres
Generally has polymers