Structure and Functions of Nucleic Acids
Structure and Functions of Nucleic Acids: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Nucleic Acids, Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Secondary Structure of DNA, Nitrogen Bases, Phosphodiester Bond, and Ribonucleic Acid.
Important Questions on Structure and Functions of Nucleic Acids
Which of the following is composed of nucleotides?
Complementary base pairs is due to formation of bonds.
Basic unit of a DNA molecule is
Name the RNA that should be most abundant in an animal cell.
What would be the length of DNA containing base pairs?
On cooling, the two separated strands of DNA again recoil. This is known as,
In the DNA model of Watson and Crick, the major grooves are sites for
The nitrogenous base is attached to the pentose sugar in a nucleoside at which carbon atom?
Compared with nucleoside, nucleotide has ___
Identify the structure formulae and select the correct option.
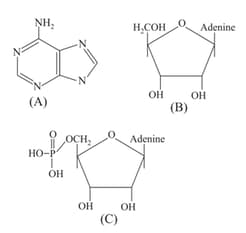
The sugars found in polynucleotides are:
Which one is not a nucleoside of :-
Which of the following component of average composition of cells that has of the total cellular mass
Thymine nitrogen base binds with which carbon atom of deoxyribose sugar :-
The area of DNA-rich A -T base pairs is called
In a double helix model of DNA, how far is each base pair from the next?
The type of RNA responsible for a proper sequence of amino acids in protein synthesis is
DNA was discovered by
