Plant Water Relations
Plant Water Relations: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Hypertonic Solutions, Hypotonic Solutions, Isotonic Solutions, Turgidity, Flaccidity, Pressure Gradient, Concentration Gradient, Osmosis, Endosmosis, Exosmosis, Osmotic Pressure, etc.
Important Questions on Plant Water Relations
In rainy seasons, the door gets swelled due to
Which of the following is/are the factor/s that affect/s chemical potential of water?
The chemical potential of pure water is less than that of a solution.
Fill in the blank with the correct answer from the bracket.
The chemical potential of pure water at normal temperature and pressure is _____. (1, 0, -1)
Define the chemical potential of water.
Match the following list with list- and select the option with correct matching.
| List -I | List - II | ||
| A. | Water potential of salt solution | I. | Positive |
| B. | Pressure potential in a normal cell | II. | Negative |
| C. | Pressure potential in a plasmolysed cell | III. | Positive |
| D. | Matric potential on the surface of the wood | IV. | Negative |
| V. | Zero |
The osmotic pressure is independent of the temperature.
Fill in the blank with the correct option provided in the bracket.
_____(Temperature/Light/Humidity) affects osmotic pressure of a solution.
Osmotic pressure is independent upon the solute concentration of a solution.
The development of concentration gradient is a prerequisite condition for active transport.
Which transport process is independent of concentration gradient?
Which of the following factor affect the osmotic pressure?
Define osmotic pressure and list factors that affect osmotic pressure.
Facilitated diffusion is independent of concentration gradient.
Define concentration gradient. How it is related to osmosis?
Based on the figure given below which of the following statements is not correct?
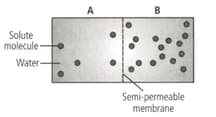
Which of the following is required for the 'uphill transport' of substances through a membrane?
Water potential is determined by
Wooden doors swell up during the rainy season is due to osmosis.
