Double Fertilization
Double Fertilization: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Double Fertilization, Triple Fusion, Mesogamy, Chalazogamy, Porogamy and, Pollen Tube Germination
Important Questions on Double Fertilization
Identify the correct option with which the part shown in the diagram below can be associated:
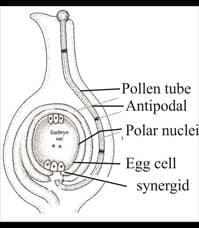
Double fertilization involves
The generative cell is destroyed by laser but a normal pollen tube is still formed because
Double fertilization and triple fusion were discovered by
Entry of pollen tube through micropyle is
Which of the following plants exhibit chalazogamy?
Fill up the blanks with suitable words
The ability of the pistil to recognise pollen is dependent on ______ components and ________ guide the entry of pollentube. This study leads to help ______ in getting _________ even in _____
A Chemicals
B. Plant breeders
C. hybrids
D. Incompatible pollination
E. Synergids
Mesogamy is the entry of pollen tube into the ovule through
Name the nuclei taking part in triple fusion.
Define triple fusion.
Give significance of double fertilization.
Write a short note on triple fusion.
Describe briefly the process of fertilization in angiosperms. Explain the changes in the cells present in the embryo sac after fertilization.
How many types of pollen tube entry are there in the ovule? Write different types of pollen tube entry in the ovule.
Write the importance of triple fusion.
What is double fertilization?
Which of the following scientists is credited with the discovery of double fertilisation in Fritillaria and Lilium?
Porogamy refers to the entry of the pollen tube in embryo sac through:
Which of the following is incorrect about double fertilization?
Read the following statements about sexual reproduction in angiosperms. How many of them are correct?
a. The number of middle layers in anther generally vary from 1-6
b. The pollen tube many enter the ovule from micropyle, chalaza or funiculus
c. Each ovule contains 8 nucleate, haploid embryosac after mitotic divisions in megaspore mother cell
d. If pollen grain of a flower falls on the stigma of another flower on the same plant, it may be referred to as self-pollination
e. Insects are often attracted by the odour of flowers rather than colour
f. Outcrossing increases genetic variability
