Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Important Questions on Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Epiblema of roots is equivalent to:
Consider the following statements regarding the given figure and select the correct one.
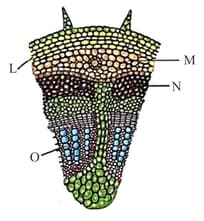
A flower represents a complex array of functionally specialised structures that differ substantially from vegetative plant body in form and cell types. Select the statement that is not true with regard to floral meristems.
Match column I with II and select the correct option from the given codes.
| I | II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Bulliform cells | (i) | Regulate opening and cells closing of stomata |
| (b) | Guard cells | (ii) | Aerating pores in the bark of plant |
| (c) | Lenticels | (iii) | Rolling in and out of leaves |
| (d) | Subsidiary cells | (iv) | Accessory cells |
Which of the following is an incorrect pair?
Study the following statements regarding the anatomy of isobilateral leaf.
Stomata are equally distributed on both the surfaces.
Certain adaxial epidermal cells are modified into bulliform cells in grasses.
The vascular bundles are radial.
Phloem is adaxially placed.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Select the correct pair out of the following.
Bundle sheath extensions in a dicot leaf and in a monocot leaf are___ and ___ respectively.
In a dorsiventral leaf, what is true regarding the position of xylem?

Identify A, B, C and D in the given transverse section of leaf of Zea mays.
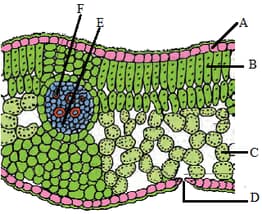
The given figure shows T.S. of Helianthus leaf with various parts labelled as A, B, C, D, E and F. Identify the parts and select the correct option.
Stomata are distributed more on the lower surface than on the upper surface in
In a dorsiventral leaf, location of palisade tissue and phloem is respectively on the_________ surfaces.
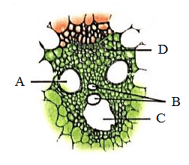
Refer to the given figure which represents a section of vascular bundle as seen in T.S. of a monocot stem and select the option that correctly labels A, B, C and D.
Lysigenous cavity in monocot stem vascular bundles develops by the dissolution of
Y- shaped arrangement of xylem vessels is found in
Bicollateral vascular bundles are found in
Select the mismatched pair.
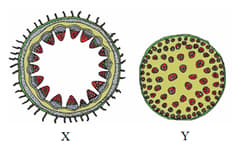
Figures X and Y represent the transverse sections of and respectively.
Select the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.

