Acyl Chlorides
Acyl Chlorides: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Reactions of Carboxylic Acids with PCl5, PCl3 and SOCl2, Oxalic Acid & Structure of Acyl Chlorides etc.
Important Questions on Acyl Chlorides
Oxalic acid is a strong reducing agent.
Draw the structure of oxalic acid.
Formic acid and acetic acid can be distinguished by reaction with
The following transformation
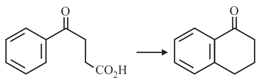
can be carried out in three steps. The reagents required for these three steps in their correct order, are:
The product obtained when acetic acid is treated with is:
Which of the following amines does not undergo acetylation?
Write Fries rearrangement.
Which is/are the correct statement(s) about the product and involved reactions?
Which of the following represents the best method for converting a carboxylic acid to an aldehyde?
The major product obtained in the following reaction is
The main product formed in the following reaction is

The compound obtained by heating salicylic acid with phenol in the presence of phosphorus oxychloride is
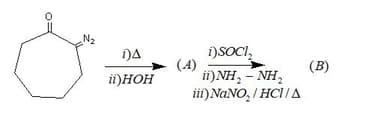
Identify the reagents A and B respectively in the following reactions
Compounds A is treated with thiionyl chloride then ammonia to give compound B. Compound B is then reacted with bromine and sodium hydroxide (tricky) to give compound. Compound C is heated to give the final product, compound D. What is the most likely structure for compound D?
Benzoyl chloride is prepared from benzoic acid by
Ethyl benzoate reacts with to give
Ethyl benzoate reacts with to give
When benzoic acid is treated with at , it gives
When benzoic acid is treated with at , it gives