Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: Overview
In this topic, we will understand the stereochemical aspects of nucleophilic substitution reactions. It sheds light on the optical activity, specific rotation, retention, chirality and enantiomers. It also discusses elimination reactions.
Important Questions on Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
What kind of reagent would be needed to resolve a racemic amine, such as 2-aminobutane?
A pure simple of -chlorobutane shows rotation of PPL by in standard conditions. When above samples is made impure by mixing its opposite form, so that the composition of the mixture become -form and -form, then what will be the observed rotation for the mixture.
The reaction which will not give chiral product(s) is :
In an reaction on chiral centres, there is:
Write an example for Walden's inversion.
Define Walden inversion.
The Walden inversion is the inversion of configuration at a chiral centre during a reaction.
If during a reaction, no bond to the stereocentre is broken, than the reaction will proceed with retention of the configuration.
The preservation of integrity of the spatial arrangement of bonds to an asymmetric centre during a chemical reaction is called inversion of configuration.
If during a reaction, the product has the same general configuration of groups around the stereocentre as that of reactant. Such a reaction is said to proceed with:
Explain the retention of configuration with an example.
If the configuration of optically active remains unchanged during the reaction, it is called _____.
Which of the following method is not used in the resolution of a racemic mixture?
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by ion? 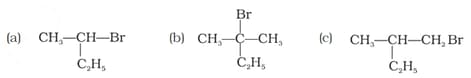
Racemic tartaric acid is optically inactive due to
A solution of (−)−1-chloro-1-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of small amount of , due to the formation of
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by ion? 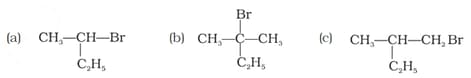
Racemic mixtures are optically _____. (inactive/active)
In case of optically active alkyl halides reactions are accompainied by _____ which results in zero rotation in polarimeter.
reaction involving inversion of configuration takes place with an optically active compound The compound is
