Opiates
Opiates: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Codeine, Diamorphine, Synthetic Opiates, Cultural Views on Drugs and, Opium and Opiate
Important Questions on Opiates
Write a short note on the cultural view of illegal drugs.
In accordance with UN world drug report, 80% opiates are produced by
Explain the mechanism of action of codeine as analgesic.
Suggest, by comparing the structures of methadone and morphine, which functional groups in their molecules are likely to be involved in binding to the opioid receptor?
Methadone binds to the opioid receptor in the same way as morphine but does not produce the euphoric effect of opiates. Deduce whether methadone is a strong analgesic or a mild analgesic?
Suggest which drug methadone or methadone hydrochloride will be more soluble in water, and which one will have higher bioavailability?
Deduce the equation for the reaction of methadone with hydrogen chloride.
Methadone is an analgesic that is commonly used in the treatment of opioid dependence. The structure of methadone is given in figure.
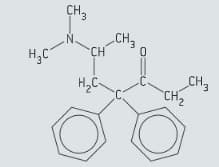
Identify by marking it with an asterisk (*) on a copy of figure, the chiral carbon atom in methadone.
Methadone is an analgesic that is commonly used in the treatment of opioid dependence. The structure of methadone is given in figure.
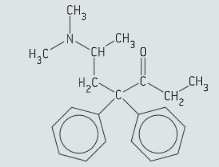
State the names of two functional groups in the molecule of methadone.
Morphine, diamorphine, and codeine are strong analgesics. Their solubility in water and lipids depends on the nature of the functional groups present in their molecules. Suggest which of the three drugs will be most soluble in lipids?
Explain, with reference to intermolecular interactions, how morphine will interact with water in solutions?
Morphine, diamorphine, and codeine are strong analgesics. Their solubility in water and lipids depends on the nature of the functional groups present in their molecules. Suggest which of these three drugs will be most soluble in water?
Suggest how the bioavailability of diamorphine will be affected by its conversion into an ionic salt?
Deduce the equation for the reaction of diamorphine with hydrogen chloride.
Diamorphine (heroin) is often administered as an ionic salt, diamorphine hydrochloride. State the name of the functional group in diamorphine that can be protonated by strong acids.
Suggest a reagent that could be used to convert morphine into diamorphine and state the name of the type of reaction taking place.
Aspirin, morphine, and diamorphine (heroin) are painkillers. Other than the phenyl group, state the name of one other functional group that is common to both aspirin and diamorphine.
Explain why heroin is a more potent drug than morphine?
Discuss two advantages and two disadvantages of using morphine and other opiates for pain relief.
