Enthalpy
Enthalpy: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Lattice Enthalpy, Enthalpy of Atomization, Endothermic Reactions at Constant Pressure & Endothermic Reactions at Constant Volume etc.
Important Questions on Enthalpy
Enthalpy change for the reaction,
The dissociation energy of bond is:
The following two reactions are known:
The value of for the following reaction
From the data of following bond energies:
Calculate the enthalpy of the following reaction in .
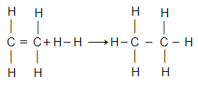
Given that bond energies of respectively and for , bond enthalpy of is:
Consider the following reactions
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
Enthalpy of formation of
For which one of the following equations is equal to for the product?
What is the enthalpy change for,
if heat of formation of are and respectively (in standard conditions)?
Enthalpy of is negative. If enthalpy of combustion of and are x and y respectively, then which relation is correct:
The values of heat of formation of are –298.2 kJ and –98.2 kJ. The enthalpy change of the reaction
will be
Bond dissociation enthalpy of respectively. The enthalpy of formation of HCl is:
Assume each reaction is carried out in an open container. For which reaction will
The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction:
will be:
[Consider the actual value instead of magnitude].
For the reaction:
at constant temperature, is:
How many of the following have standard heat of formation value of zero.
Why heat of a reaction of an exothermic process at constant volume is negative and equal to change in internal energy?
For an exothermic reaction at constant volume, the heat of the reaction is equal to internal energy with a negative sign.
Why heat of a reaction of an endothermic process at constant volume is positive and equal to change in internal energy?
The heat of a reaction at constant volume for an endothermic process is equal to and it has a positive value.
The heat of reaction for an endothermic reaction at constant volume in equilibrium is more than the heat of reaction at constant pressure at . Calculate the ratio of equilibrium constants and .
Predict the signs of and for an exothermic reaction at constant volume with reversible work.
