Thermodynamic Properties
Thermodynamic Properties: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Common Terms in Thermodynamics, System in Thermodynamics, Surroundings in Thermodynamics, Boundary in Thermodynamics, Isolated System, Closed System, Open System, Intensive Property, Extensive Property, etc.
Important Questions on Thermodynamic Properties
Which of the following are not state functions?
Which of the following option is correct match for extensive and intensive property:
Which of the following pairs belongs to extensive property?
Which of the following statements is true for an open system?
An isolated system is that system in which:
As shown in the figure, the walls of the beakers will act as_____ ?

We could have chosen only the reactants as system then walls of the beakers will act as _____ ?
The wall that separates the system from the surroundings is called _____?
A system in thermodynamics refers to that part of universe in which observations are made and remaining universe constitutes the _____ ?
Establish a relationship between the surroundings, system and universe?
A closed system is that which?
Choose the one which is not an Extensive property
Isolated system is a system in which energy and matter is not exchanged with surroundings.
Which of the following are not state functions?
Which one of the following pairs does not represent example for intensive property?
Which of the following is not an extensive property?
Explain the term state function. Give two examples of state functions and two examples of path functions.
Define the terms: system, surroundings, open system, closed system, isolated system, exothermic reactions, endothermic reactions, extensive properties and intensive properties.
Identify the inappropriate relationship between and ?
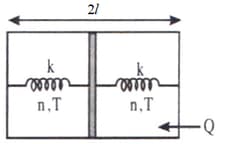
Determine the heat Q' given away to the thermostat by the left part of the piston if a horizontally insulated cylindrical vessel of length 2ℓ is separated by a thin insulating piston into two equal parts each of which contains n moles of an ideal monoatomic gas at temperature T and the left part is in contact with a thermostat (a device which maintains a constant temperature). Moreover, the piston is connected to the end faces of the vessel by undeformed springs of force constant k each.