Elevation of Boiling Point
Elevation of Boiling Point: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as boiling point, elevation of boiling point and molal boiling point elevation constant using molar heat of vapourisation.
Important Questions on Elevation of Boiling Point
A solution containing of a substance in of diethyl ether boils at whereas, pure ether boils at
The molecular mass of the solute would be: (for ether)
If an equimolar solution of , and in water have boiling point of and respectively then
If the boiling points of two solvents and (having same molecular weights) are in the ratio and their enthalpy of vaporizations are in the ratio , then the boiling point elevation constant of is times the boiling point elevation constant of . The value of is (nearest integer).
The vapour pressure vs. temperature curve for a solution solvent system is shown below.
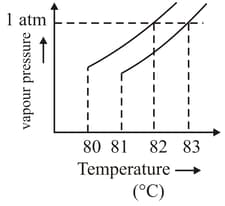
The boiling point of the solvent is _____°C.
Calculate the elevation in boiling point of an aqueous solution of molal monobasic acid, which undergoes ionization is
Calculate the molal elevation boiling point constant of a solution containing of urea in water and boils at .
The molal elevation constant for water is . Calculate the boiling point of solution made by dissolving of urea () in of water.
The rise in boiling point of a solution containing of glucose in of solvent is . The molal elevation constant of the liquid is
The aqueous solution that shows the maximum boiling point elevation is [Assume identical conditions]
Calculate the boiling point of solution when of was dissolved in of water, assuming undergoes complete ionization.
of urea and of glucose are dissolved of water find the boiling point of solutions and pure water boiling point is . for water is .
A student observed that the boiling of the water containing of was . If more water is added to the solution, will its boiling point increase or decrease? Give reason.
of aq. Solution of urea having density is found to have , if temperature of this solution increase to then calculate amount of water which must have gone into vapour state up to this point. Givenfor water
Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the minimum boiling point?
Two liquids and boil at and respectively. Which of them has a higher vapour pressure at ?
Why boiling point of water is increased on the addition of sodium chloride into it?
What will happen to the boiling point of a solution if the weight of the solute dissolved is doubled but the weight of solvent taken is halved?
Which solution has maximum boiling point?
Define molal elevation constant or ebullioscopic constant.
